List of the most distant astronomical objects

This article documents the most distant astronomical objects discovered and verified so far, and the time periods in which they were so classified.
For comparisons with the light travel distance of the astronomical objects listed below, the age of the universe since the Big Bang is currently estimated as 13.787±0.020 Gyr.[1]
Distances to remote objects, other than those in nearby galaxies, are nearly always inferred by measuring the cosmological redshift of their light. By their nature, very distant objects tend to be very faint, and these distance determinations are difficult and subject to errors. An important distinction is whether the distance is determined via spectroscopy or using a photometric redshift technique. The former is generally both more precise and also more reliable, in the sense that photometric redshifts are more prone to being wrong due to confusion with lower redshift sources that may have unusual spectra. For that reason, a spectroscopic redshift is conventionally regarded as being necessary for an object's distance to be considered definitely known, whereas photometrically determined redshifts identify "candidate" very distant sources. Here, this distinction is indicated by a "p" subscript for photometric redshifts.
The proper distance provides a measurement of how far a galaxy is at a fixed moment in time. At the present time the proper distance equals the comoving distance since the cosmological scale factor has value one: . The proper distance represents the distance obtained as if one were able to freeze the flow of time (set in the FLRW metric) and walk all the way to a galaxy while using a meter stick.[2] For practical reasons, the proper distance is calculated as the distance traveled by light (set in the FLRW metric) from the time of emission by a galaxy to the time an observer (on Earth) receives the light signal. It differs from the “light travel distance” since the proper distance takes into account the expansion of the universe, i.e. the space expands as the light travels through it, resulting in numerical values which locate the most distant galaxies beyond the Hubble sphere and therefore with recession velocities greater than the speed of light c.[3]
Most distant spectroscopically-confirmed objects
[edit]| Image | Name | Redshift (z) |
Light travel distance§ (Gly)[4][5][6][7] |
Proper distance
(Gly) |
Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
JADES-GS-z14-0 | z = 14.32+0.08 −0.20 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec.[8] | ||
| JADES-GS-z14-1 | z = 13.90+0.17 −0.17 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec.[9] | |||

|
JADES-GS-z13-0 | z = 13.20+0.04 −0.07 |
13.576[4] / 13.596[5] / 13.474[6] / 13.473[7] | 33.6 | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec.[10] |

|
UNCOVER-z13 | z = 13.079+0.014 −0.001 |
13.51 | 32.56† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec.[11] |
| JADES-GS-z12-0 | z = 12.63+0.24 −0.08 |
13.556[4] / 13.576[5] / 13.454[6] / 13.453[7] | 32.34† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRCam [10] and JWST/NIRSpec,[12] and CIII] line emission with JWST/NIRSpec.[12] Most distant spectroscopic redshift from emission lines; most distant detection of non-primordial elements (C, O, Ne). | |

|
UNCOVER-z12 | z = 12.393+0.004 −0.001 |
13.48 | 32.21† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec.[11] |

|
GLASS-z12 | z = 12.117+0.01 −0.01 |
13.536[4] / 13.556[5] / 13.434[6] / 13.433[7] | 33.2 | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST/NIRCam, confirmed by ALMA detection of [O III] emission[13] |

|
UDFj-39546284 | z = 11.58+0.05 −0.05 |
13.512[4] / 13.532[5] / 13.410[6] / 13.409[7] | 31.77† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec.[10] |
| CEERS J141946.36+525632.8 (Maisie's Galaxy) |
z = 11.44+0.09 −0.08 |
13.4 | 31.69† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST | |
| CEERS2 588 |
z = 11.04 | 13.45 | 31.45† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST | |

|
GN-z11 | z = 10.6034 ± 0.0013 | 13.481[4] / 13.501[5] / 13.380[6] / 13.379[7] | 31.18† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy; detection of the Lyman break with HST at 5.5σ[16] and carbon emission lines with Keck/MOSFIRE at 5.3σ.[17] Conclusive redshift by JWST in February 2023[12] |
| JADES-GS-z10-0 UDFj-39546284 | z = 10.38+0.07 −0.06 |
13.449[4] / 13.469[5] / 13.348[6] / 13.347[7] | 31.04† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec[10] | |

|
JD1 | z = 9.793±0.002 | 13.409[4] / 13.429[5] / 13.308[6] / 13.307[7] | 30.12† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy, detection of the Lyman break with JWST/NIRSpec[18] |
| Gz9p3 | z=9.3127 ± 0.0002 | 13.277[4] | 30.27† | Galaxy | A galaxy merger with a redshift estimated from [OII], Ne and H emission lines detected with JWST.[19] | |

|
MACS1149-JD1 | z = 9.1096±0.0006 | 13.361[4] / 13.381[5] / 13.261[6] / 13.260[7] | 30.37 | Galaxy | Detection of hydrogen emission line with the VLT, and oxygen line with ALMA[20] |

|
EGSY8p7 | z = 8.683+0.001 −0.004 |
13.325[4] / 13.345[5] / 13.225[6] / 13.224[7] | 30.05 | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter; detection of Lyman-alpha with Keck/MOSFIRE at 7.5σ confidence[21] |
| SMACS-4590 | z = 8.496 | 13.308[4] / 13.328[5] / 13.208[6] / 13.207[7] | 29.71† | Galaxy | Detection of hydrogen, oxygen, and neon emission lines with JWST/NIRSpec[22][23][24][25] | |
| A2744 YD4 | z = 8.38 | 13.297[4] / 13.317[5] / 13.197[6] / 13.196[7] | 29.50† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha and [O III] emission detected with ALMA at 4.0σ confidence[26] | |
| MACS0416 Y1 | z = 8.3118±0.0003 | 13.290[4] / 13.310[5] / 13.190[6] / 13.189[7] | 29.44† | Galaxy | [O III] emission detected with ALMA at 6.3σ confidence[27] | |
| GRB 090423 | z = 8.23+0.06 −0.07 |
13.282[4] / 13.302[5] / 13.182[6] / 13.181[7] | 30 | Gamma-ray burst | Lyman-alpha break detected[28] | |
| RXJ2129-11002 | z = 8.16±0.01 | 13.175[4] | 29.31† | Galaxy | [O III] doublet, Hβ, and [O II] doublet as well as Lyman-alpha break detected with JWST/NIRSpec prism[29] | |
| RXJ2129-11022 | z = 8.15±0.01 | 13.174[4] | 29.30† | Galaxy | [O III] doublet and Hβ as well as Lyman-alpha break detected with JWST/NIRSpec prism[29] | |

|
EGS-zs8-1 | z = 7.7302±0.0006 | 13.228[4] / 13.248[5] / 13.129[6] / 13.128[7] | 29.5 | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy[30] |
| SMACS-6355 | z = 7.665 | 13.221[4] / 13.241[5] / 13.121[6] / 13.120[7] | 28.83 | Galaxy | Detection of hydrogen, oxygen, and neon emission lines with JWST/NIRSpec[22][23][24][25] | |
| z7_GSD_3811 | z = 7.6637±0.0011 | 13.221[4] / 13.240[5] / 13.121[6] / 13.120[7] | 28.83† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[31] | |
| SMACS-10612 | z = 7.658 | 13.221[4] / 13.241[5] / 13.120[6] / 13.119[7] | 28.83† | Galaxy | Detection of hydrogen, oxygen, and neon emission lines with JWST/NIRSpec[22][23][24]>[25] | |
| QSO J0313–1806 | z = 7.6423±0.0013 | 13.218[4] / 13.238[5] / 13.119[6] / 13.118[7] | 30 | Quasar | Lyman-alpha break detected[32] | |
| ULAS J1342+0928 | z = 7.5413±0.0007 | 13.206[4] / 13.226[5] / 13.107[6] / 13.106[7] | 29.36 | Quasar | Redshift estimated from [C II] emission[33] | |

|
z8_GND_5296 | z = 7.51 | 13.202[4] / 13.222[5] / 13.103[6] / 13.102[7] | 30.01 | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[34] |

|
A1689-zD1 | z = 7.5±0.2 | 13.201[4] / 13.221[5] / 13.102[6] / 13.101[7] | 30 | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy[35] |
| GS2_1406 | z = 7.452±0.003 | 13.195[4] / 13.215[5] / 13.096[6] / 13.095[7] | 28.62† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[36] | |

|
GN-108036 | z = 7.213 | 13.164[4] / 13.184[5] / 13.065[6] / 13.064[7] | 29 | Galaxy | Lyman alpha emitter[37] |
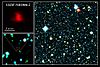
|
SXDF-NB1006-2 | z = 7.2120±0.0003 | 13.164[4] / 13.184[5] / 13.065[6] / 13.064[7] | 29 | Galaxy | [O III] emission detected[38] |

|
BDF-3299 | z = 7.109±0.002 | 13.149[4] / 13.169[5] / 13.051[6] / 13.050[7] | 28.25 | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy[39] |

|
ULAS J1120+0641 | z = 7.085±0.003 | 13.146[4] / 13.166[5] / 13.048[6] / 13.047[7] | 29.85 | Quasar | Redshift estimated from Si III]+C III] and Mg II emission lines[40] |
| A1703 zD6 | z = 7.045±0.004 | 13.140[4] / 13.160[5] / 13.042[6] / 13.041[7] | 29 | Galaxy | Gravitationally-lensed Lyman-alpha emitter[41] | |
| BDF-521 | z = 7.008±0.002 | 13.135[4] / 13.155[5] / 13.037[6] / 13.036[7] | 28.43† | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy[39] | |
| G2_1408 | z = 6.972±0.002 | 13.130[4] / 13.150[5] / 13.032[6] / 13.030[7] | 28.10† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[42] | |

|
IOK-1 | z = 6.965 | 13.129[4] / 13.149[5] / 13.030[6] / 13.029[7] | 28.09† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[37] |

|
LAE J095950.99+021219.1 | z = 6.944 | 13.126[4] / 13.146[5] / 13.028[6] / 13.027[7] | 28.07† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[43] |
| SDF-46975 | z = 6.844 | 13.111[4] / 13.131[5] / 13.013[6] / 13.012[7] | 27.95† | Galaxy | Lyman-alpha emitter[37] | |
| PSO J172.3556+18.7734 | z = 6.823+0.003 −0.001 |
13.107[4] / 13.127[5] / 13.010[6] / 13.009[7] | 27.93† | Quasar (astrophysical jet) |
Redshift estimated from Mg II emission[44] | |
|
§ The tabulated distance is the light travel distance, which has no direct physical significance. See discussion at distance measures and Observable Universe † Numeric value obtained using Wright (2006)[5] with = 70, = 0.30, = 0.70. | ||||||
Candidate most distant objects
[edit]Since the beginning of the James Webb Space Telescope's (JWST) science operations in June 2022, numerous distant galaxies far beyond what could be seen by the Hubble Space Telescope (z = 11) have been discovered thanks to the JWST's capability of seeing far into the infrared.[45][46] Previously in 2012, there were about 50 possible objects z = 8 or farther, and another 100 candidates at z = 7, based on photometric redshift estimates released by the Hubble eXtreme Deep Field (XDF) project from observations made between mid-2002 and December 2012.[47] Some objects included here have been observed spectroscopically, but had only one emission line tentatively detected, and are therefore still considered candidates by researchers.[48][49]
| Name | Redshift (z) |
Light travel distance§ (Gly) |
Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F200DB-045 | zp = 20.4+0.3 −0.3[46] or 0.70+0.19 −0.55[45] or 0.40+0.15 −0.26[50] |
13.725[4] / 13.745[5] / 13.623[6] / 13.621[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] NOTE: The redshift value of the galaxy presented by the procedure in one study[45] may differ from the values presented in other studies using different procedures.[46][51][50] |
| F200DB-175 | zp = 16.2+0.3 −0.0 |
13.657[4] / 13.677[5] / 13.555[6] / 13.554[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| S5-z17-1 | z = 16.0089±0.0004 or 4.6108±0.0001 |
13.653[4] / 13.673[5] / 13.551[6] / 13.550[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST; tentative (5.1σ) ALMA detection of a single emission line possibly attributed to either [C II] (z = 4.6108±0.0001) or [O III] (z = 16.0089±0.0004).[48][49] |
| F150DB-041 | zp = 16.0+0.2 −0.2[46] or 3.70+0.02 −0.59[45] |
13.653[4] / 13.673[5] / 13.551[6] / 13.549[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46][45] |
| SMACS-z16a | zp = 15.92+0.17 −0.15[52] or 2.96+0.73 −0.21[45] |
13.651[4] / 13.671[5] / 13.549[6] / 13.548[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[52][45] |
| F200DB-015 | zp = 15.8+3.4 −0.1 |
13.648[4] / 13.668[5] / 13.546[6] / 13.545[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F200DB-181 | zp = 15.8+0.5 −0.3 |
13.648[4] / 13.668[5] / 13.546[6] / 13.545[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F200DB-159 | zp = 15.8+4.0 −15.2 |
13.648[4] / 13.668[5] / 13.546[6] / 13.545[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F200DB-086 | zp = 15.4+0.6 −14.6[46] or 3.53+10.28 −1.84[45] |
13.639[4] / 13.659[5] / 13.537[6] / 13.536[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46][45] |
| SMACS-z16b | zp = 15.32+0.16 −0.13[52] or 15.39+0.18 −0.26[45] |
13.637[4] / 13.657[5] / 13.535[6] / 13.534[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[52][45] |
| F150DB-048 | zp = 15.0+0.2 −0.8 |
13.629[4] / 13.649[5] / 13.527[6] / 13.526[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DB-007 | zp = 14.6+0.4 −0.4 |
13.619[4] / 13.639[5] / 13.517[6] / 13.516[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DB-004 | zp = 14.0+0.4 −2.0 |
13.602[4] / 13.622[5] / 13.500[6] / 13.499[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DB-079 | zp = 13.8+0.5 −1.9 |
13.596[4] / 13.616[5] / 13.494[6] / 13.493[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DA-007 | zp = 13.4+0.6 −2.0 |
13.583[4] / 13.603[5] / 13.481[6] / 13.480[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DA-053 | zp = 13.4+0.3 −2.3 |
13.583[4] / 13.603[5] / 13.481[6] / 13.480[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DA-050 | zp = 13.4+0.6 −10.0 |
13.583[4] / 13.603[5] / 13.481[6] / 13.480[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DA-058 | zp = 13.4+0.6 −12.5[46] 3.42+0.30 −0.20[45] |
13.583[4] / 13.603[5] / 13.481[6] / 13.480[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46][45] |
| F150DA-038 | zp = 13.4+0.4 −13.2 |
13.583[4] / 13.603[5] / 13.481[6] / 13.480[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| HD1 | z = 13.27 | 13.579[4] / 13.599[5] / 13.477[6] / 13.476[7] | Galaxy | Not yet spectroscopically confirmed. Guinness World Record of the most distant confirmed galaxy Lyman-break galaxy (5σ confidence) followed with a tentative ALMA detection of a single [O III] oxygen emission line only (4σ confidence)[53] |
| F150DA-010 | zp = 12.8+0.6 −1.5 |
13.562[4] / 13.582[5] / 13.460[6] / 13.459[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| S5-z12-1 | zp = 12.57+1.23 −0.46 |
13.553[4] / 13.573[5] / 13.452[6] / 13.451[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[48] |
| CEERS-27535 4 | zp = 12.56+1.75 −0.27 |
13.553[4] / 13.573[5] / 13.452[6] / 13.451[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| SMACS-1566 | zp = 12.29+1.50 −0.44 |
13.542[4] / 13.562[5] / 13.441[6] / 13.440[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| SMACS-z12b (F150DA-077) |
zp = 12.26+0.17 −0.16[52][45] or 13.4+0.4 −1.7[46] |
13.541[4] / 13.561[5] / 13.440[6] / 13.439[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[52][45][46] |
| SMACS-z12a | zp = 12.20+0.21 −0.12 |
13.539[4] / 13.559[5] / 13.437[6] / 13.436[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[52][45] |
| CR2-z12-4 | zp = 12.08+2.11 −1.25 |
13.534[4] / 13.554[5] / 13.432[6] / 13.431[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[48] |
| SMACS-10566 | zp = 12.03+0.57 −0.26 |
13.532[4] / 13.552[5] / 13.430[6] / 13.429[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| XDFH-2395446286 | zp = 12.0+0.1 −0.2 |
13.530[4] / 13.550[5] / 13.429[6] / 13.428[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy detected by JWST and Hubble[55] |
| CR2-z12-2 | zp = 11.96+1.44 −0.87 |
13.529[4] / 13.549[5] / 13.427[6] / 13.426[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[48] |
| 9-BUSCAR | zp = 11.91+0.10 −0.22 |
13.527[4] / 13.547[5] / 13.425[6] / 13.424[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[56] |
| SMACS-8347 | zp = 11.90+0.27 −0.39 |
13.526[4] / 13.546[5] / 13.425[6] / 13.424[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| CEERS-26409 4 | zp = 11.90+1.60 −0.70 |
13.526[4] / 13.546[5] / 13.425[6] / 13.424[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| F150DB-069 | zp = 11.8+1.7 −0.2 |
13.522[4] / 13.542[5] / 13.420[6] / 13.419[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| XDFH-2334046578 | zp = 11.8+0.4 −0.5 |
13.522[4] / 13.542[5] / 13.420[6] / 13.419[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy detected by JWST and Hubble[55] |
| CR2-z12-3 | zp = 11.66+0.69 −0.71 |
13.515[4] / 13.535[5] / 13.414[6] / 13.413[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[48] |
| CR2-z12-1 | zp = 11.63+0.51 −0.53 |
13.514[4] / 13.534[5] / 13.413[6] / 13.412[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[48] |
| F150DB-088 | zp = 11.6+0.3 −0.2 |
13.513[4] / 13.533[5] / 13.411[6] / 13.410[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DB-084 | zp = 11.6+0.4 −0.4 |
13.513[4] / 13.533[5] / 13.411[6] / 13.410[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DB-044 | zp = 11.4+0.4 −11.3 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| XDFH-2404647339 | zp = 11.4+0.4 −0.5 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy detected by JWST and Hubble[55] |
| F150DB-075 | zp = 11.4+0.4 −0.1[46] 0.04+0.01 −0.01[45] |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46][45] |
| F150DA-062 | zp = 11.4+0.3 −0.3[46] 1.78+0.20 −0.08[45] |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46][45] |
| CEERS-127682 | zp = 11.40+0.59 −0.51 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| CEERS-5268 2 | zp = 11.40+0.30 −1.11 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] |
| F150DA-060 | zp = 11.4+0.6 −8.2 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DA-031 | zp = 11.4+1.0 −8.2 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DA-052 | zp = 11.4+0.8 −10.6 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| F150DB-054 | zp = 11.4+0.5 −10.8 |
13.503[4] / 13.523[5] / 13.402[6] / 13.401[7] | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] |
| SMACS-z11d | zp = 11.28±0.32 or 2.35+0.30 −0.67 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[45] | |
| CEERS-77241 | zp = 11.27+0.39 −0.70 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] | |
| CEERS-6647 | zp = 11.27+0.58 −0.28 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] | |
| CEERS-622 4 | zp = 11.27+0.48 −0.60 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] | |
| SMACS-z11c | zp = 11.22±0.32 or 3.84+0.05 −0.04 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[45] | |
| SMACS-z11b | zp = 11.22±0.56 or 6.94+0.07 −0.07 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[45] | |
| F150DA-005 | zp = 11.2+0.4 −0.3 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] | |
| F150DA-020 | zp = 11.2+0.2 −7.9 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] | |
| CEERS-61486 | zp = 11.15+0.37 −0.35 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[54] | |
| SMACS-z11e (F150DA-081) |
zp = 11.10+0.21 −0.34[45] or 13.4+0.6 −2.2[46] |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[45][46] | |
| SMACS-z11a | zp = 11.05+0.09 −0.08[52] or 1.73+0.18 −0.04[45] |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[52][45] | |
| CR3-z12-1 | zp = 11.05+2.24 −0.47 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[48] | |
| F150DA-026 | zp = 11.0+0.5 −0.3 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] | |
| F150DA-036 | zp = 11.0+0.4 −7.8 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] | |
| SMACS-z10e | zp = 10.89+0.16 −0.14[52] or 1.38+1.37 −0.24[45] |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[52][45] | |
| F150DB-040 | zp = 10.8+0.3 −0.2 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[46] | |
| EGS-14506 | zp = 10.71+0.34 −0.62 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[57] | |
| MACS0647-JD | zp = 10.6±0.3 | Galaxy | Gravitationally lensed into three images by a galaxy cluster; detected by JWST and Hubble[58][59] | |
| GLASS-z10 (GLASS-1698)[54] |
z = 10.38 | Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST; tentative (4.4σ) ALMA detection of [O III] emission line only[60][61] | |
| EGS-7860 | zp = 10.11+0.60 −0.82 |
Galaxy | Lyman-break galaxy discovered by JWST[57] | |
| SPT0615-JD | zp = 9.9+0.8 −0.6 |
13.419[4] | Galaxy | [62] |
| A2744-JD | zp≅9.8 | 13.412[4] | Galaxy | Galaxy is being magnified and lensed into three multiple images, geometrically supporting its redshift.[63][64] |
| MACS1149-JD1 | zp≅9.6 | 13.398[4][65] | Candidate galaxy or protogalaxy | [66] |
| GRB 090429B | zp≅9.4 | 13.383[4][67] | Gamma-ray burst | [68] The photometric redshift in this instance has quite large uncertainty, with the lower limit for the redshift being z>7. |
| UDFy-33436598 | zp≅8.6 | 13.317[4] | Candidate galaxy or protogalaxy | [69] |
| UDFy-38135539 | zp≅8.6 | 13.317[4] | Candidate galaxy or protogalaxy | A spectroscopic redshift of z = 8.55 was claimed for this source in 2010,[70] but has subsequently been shown to be mistaken.[71] |
| BoRG-58 | zp≅8 | 13.258[4] | Galaxy cluster or protocluster | Protocluster candidate[72] |
|
§ The tabulated distance is the light travel distance, which has no direct physical significance. See discussion at distance measures and Observable Universe | ||||
List of most distant objects by type
[edit]This article needs to be updated. (June 2023) |
| Type | Object | Redshift (distance) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any astronomical object, no matter what type | JADES-GS-z14-0 | z = 14.32 | Most distant galaxy with a spectroscopically confirmed redshift as of 2024[update].[8] |
| Galaxy or protogalaxy | |||
| Galaxy cluster | CL J1001+0220 | z ≅ 2.506 | As of 2016[73] |
| Galaxy supercluster | Hyperion proto-supercluster | z = 2.45 | This supercluster at the time of its discovery in 2018 was the earliest and largest proto-supercluster found to date.[74] |
| Galaxy protocluster | A2744z7p9OD | z = 7.88 | This protocluster at the time of its discovery in 2023 was the most distant protocluster found and spectroscopically confirmed to date.[75] |
| Quasar | UHZ1 | z ~ 10.0 | [76] |
| Black hole | GN-z11 | z = 10.6034±0.0013[77] | [78][79][80] |
| Star or protostar or post-stellar corpse (detected by an event) |
Progenitor of GRB 090423 | z = 8.2 | [81][28] Note, GRB 090429B has a photometric redshift zp≅9.4,[82] and so is most likely more distant than GRB 090423, but is lacking spectroscopic confirmation. Estimated an approximate distance of 13 billion lightyears from Earth |
| Star or protostar or post-stellar corpse (detected as a star) |
WHL0137-LS (Earendel) | z = 6.2 ± 0.1 (12.9 Gly) |
Most distant individual star detected (March, 2022).[83][84]
Previous records include SDSS J1229+1122[85] and MACS J1149 Lensed Star 1.[86] |
| Star cluster | The Sparkler | z = 1.378 (13.9 Gly) |
Galaxy with globular clusters gravitationally lensed in SMACS J0723.3-7327[87] |
| System of star clusters | |||
| X-ray jet | PJ352–15 quasar jet | z = 5.831 (12.7 Gly)[88] |
The previous recordholder was at 12.4 Gly.[89][90] |
| Microquasar | XMMU J004243.6+412519 | (2.5 Mly) | First extragalactic microquasar discovered[91][92][93] |
| Nebula-like object | Himiko | z = 6.595 | Possibly one of the largest objects in the early universe.[94][95] |
| Magnetic field | 9io9 | z = 2.554 (11.1 Gly) | Observations from ALMA has shown that the lensed galaxy 9io9 contains a magnetic field. |
| Planet | SWEEPS-11 / SWEEPS-04 | (27,710 ly) | [96]
|
| Type | Event | Redshift | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma-ray burst | GRB 090423 | z = 8.2 | [81][28] Note, GRB 090429B has a photometric redshift zp≅9.4,[82] and so is most likely more distant than GRB 090423, but is lacking spectroscopic confirmation. |
| Core collapse supernova | SN 1000+0216 | z = 3.8993 | [100] |
| Type Ia supernova | SN UDS10Wil | z = 1.914 | [101] |
| Type Ia supernova | SN SCP-0401 (Mingus) |
z = 1.71 | First observed in 2004, it was not until 2013 that it could be identified as a Type-Ia SN.[102][103] |
| Cosmic Decoupling | Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation creation | z~1000 to 1089 | [104][105] |
Timeline of most distant astronomical object recordholders
[edit]Objects in this list were found to be the most distant object at the time of determination of their distance. This is frequently not the same as the date of their discovery.
Distances to astronomical objects may be determined through parallax measurements, use of standard references such as cepheid variables or Type Ia supernovas, or redshift measurement. Spectroscopic redshift measurement is preferred, while photometric redshift measurement is also used to identify candidate high redshift sources. The symbol z represents redshift.
| Object | Type | Date | Distance (z = Redshift) |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JADES-GS-z14-0 | Galaxy | 2024–present | z = 14.32 | |
| JADES-GS-z13-0 | Galaxy | 2022–2024 | z = 13.20 | [10] |
| GN-z11 | Galaxy | 2016–2022 | z = 10.6 | [16][17] |
| EGSY8p7 | Galaxy | 2015−2016 | z = 8.68 | [106][107][108][109] |
| Progenitor of GRB 090423 / Remnant of GRB 090423 | Gamma-ray burst progenitor / Gamma-ray burst remnant | 2009–2015 | z = 8.2 | [28][110] |
| IOK-1 | Galaxy | 2006 − 2009 | z = 6.96 | [110][111][112][113] |
| SDF J132522.3+273520 | Galaxy | 2005 − 2006 | z = 6.597 | [113][114] |
| SDF J132418.3+271455 | Galaxy | 2003 − 2005 | z = 6.578 | [114][115][116][117] |
| HCM-6A | Galaxy | 2002 − 2003 | z = 6.56 | The galaxy is lensed by galaxy cluster Abell 370. This was the first non-quasar galaxy found to exceed redshift 6. It exceeded the redshift of quasar SDSSp J103027.10+052455.0 of z = 6.28[115][116][118][119][120][121] |
| SDSS J1030+0524 (SDSSp J103027.10+052455.0) |
Quasar | 2001 − 2002 | z = 6.28 | [122][123][124][125][126][127] |
| SDSS 1044–0125 (SDSSp J104433.04–012502.2) |
Quasar | 2000 − 2001 | z = 5.82 | [128][129][126][127][130][131][132] |
| SSA22-HCM1 | Galaxy | 1999–2000 | z>=5.74 | [129][133] |
| HDF 4-473.0 | Galaxy | 1998–1999 | z = 5.60 | [133] |
| RD1 (0140+326 RD1) | Galaxy | 1998 | z = 5.34 | [134][135][136][133][137] |
| CL 1358+62 G1 & CL 1358+62 G2 | Galaxies | 1997 − 1998 | z = 4.92 | These were the most remote objects discovered at the time. The pair of galaxies were found lensed by galaxy cluster CL1358+62 (z = 0.33). This was the first time since 1964 that something other than a quasar held the record for being the most distant object in the universe.[135][138][139][136][133][140] |
| PC 1247–3406 | Quasar | 1991 − 1997 | z = 4.897 | [141][128][142][143][144][145] |
| PC 1158+4635 | Quasar | 1989 − 1991 | z = 4.73 | [128][145][146][147][148][149] |
| Q0051–279 | Quasar | 1987 − 1989 | z = 4.43 | [150][146][149][151][152][153] |
| Q0000–26 (QSO B0000–26) |
Quasar | 1987 | z = 4.11 | [150][146][154] |
| PC 0910+5625 (QSO B0910+5625) |
Quasar | 1987 | z = 4.04 | This was the second quasar discovered with a redshift over 4.[128][146][155][156] |
| Q0046–293 (QSO J0048–2903) |
Quasar | 1987 | z = 4.01 | [150][146][155][157][158] |
| Q1208+1011 (QSO B1208+1011) |
Quasar | 1986 − 1987 | z = 3.80 | This is a gravitationally-lensed double-image quasar, and at the time of discovery to 1991, had the least angular separation between images, 0.45″.[155][159][160] |
| PKS 2000-330 (QSO J2003–3251, Q2000–330) |
Quasar | 1982 − 1986 | z = 3.78 | [155][161][162] |
| OQ172 (QSO B1442+101) |
Quasar | 1974 − 1982 | z = 3.53 | [163][164][165] |
| OH471 (QSO B0642+449) |
Quasar | 1973 − 1974 | z = 3.408 | Nickname was "the blaze marking the edge of the universe".[163][165][166][167][168] |
| 4C 05.34 | Quasar | 1970 − 1973 | z = 2.877 | Its redshift was so much greater than the previous record that it was believed to be erroneous, or spurious.[165][169][170][171] |
| 5C 02.56 (7C 105517.75+495540.95) |
Quasar | 1968 − 1970 | z = 2.399 | [140][171][172] |
| 4C 25.05 (4C 25.5) |
Quasar | 1968 | z = 2.358 | [140][171][173] |
| PKS 0237–23 (QSO B0237–2321) |
Quasar | 1967 − 1968 | z = 2.225 | [169][173][174][175][176] |
| 4C 12.39 (Q1116+12, PKS 1116+12) |
Quasar | 1966 − 1967 | z = 2.1291 | [140][176][177][178] |
| 4C 01.02 (Q0106+01, PKS 0106+1) |
Quasar | 1965 − 1966 | z = 2.0990 | [140][176][177][179] |
| 3C 9 | Quasar | 1965 | z = 2.018 | [176][180][181][182][183][184] |
| 3C 147 | Quasar | 1964 − 1965 | z = 0.545 | [185][186][187][188] |
| 3C 295 | Radio galaxy | 1960 − 1964 | z = 0.461 | [133][140][189][190][191] |
| LEDA 25177 (MCG+01-23-008) | Brightest cluster galaxy | 1951 − 1960 | z = 0.2 (V = 61000 km/s) |
This galaxy lies in the Hydra Supercluster. It is located at B1950.0 08h 55m 4s +03° 21′ and is the BCG of the fainter Hydra Cluster Cl 0855+0321 (ACO 732).[133][191][192][193][194][195][196] |
| LEDA 51975 (MCG+05-34-069) | Brightest cluster galaxy | 1936 – | z = 0.13 (V = 39000 km/s) |
The brightest cluster galaxy of the Bootes Cluster (ACO 1930), an elliptical galaxy at B1950.0 14h 30m 6s +31° 46′ apparent magnitude 17.8, was found by Milton L. Humason in 1936 to have a 40,000 km/s recessional redshift velocity.[195][197][198] |
| LEDA 20221 (MCG+06-16-021) | Brightest cluster galaxy | 1932 – | z = 0.075 (V = 23000 km/s) |
This is the BCG of the Gemini Cluster (ACO 568) and was located at B1950.0 07h 05m 0s +35° 04′[197][199] |
| BCG of WMH Christie's Leo Cluster | Brightest cluster galaxy | 1931 − 1932 | z = (V = 19700 km/s) |
[199][200][201][202] |
| BCG of Baede's Ursa Major Cluster | Brightest cluster galaxy | 1930 − 1931 | z = (V = 11700 km/s) |
[202][203] |
| NGC 4860 | Galaxy | 1929 − 1930 | z = 0.026 (V = 7800 km/s) |
[203][204][205] |
| NGC 7619 | Galaxy | 1929 | z = 0.012 (V = 3779 km/s) |
Using redshift measurements, NGC 7619 was the highest at the time of measurement. At the time of announcement, it was not yet accepted as a general guide to distance, however, later in the year, Edwin Hubble described redshift in relation to distance, which became accepted widely as an inferred distance.[204][206][207] |
| NGC 584 (Dreyer nebula 584) |
Galaxy | 1921 − 1929 | z = 0.006 (V = 1800 km/s) |
At the time, nebula had yet to be accepted as independent galaxies. However, in 1923, galaxies were generally recognized as external to the Milky Way.[195][204][206][208][209][210][211] |
| M104 (NGC 4594) | Galaxy | 1913 − 1921 | z = 0.004 (V = 1180 km/s) |
This was the second galaxy whose redshift was determined; the first being Andromeda – which is approaching us and thus cannot have its redshift used to infer distance. Both were measured by Vesto Melvin Slipher. At this time, nebula had yet to be accepted as independent galaxies. NGC 4594 was measured originally as 1000 km/s, then refined to 1100, and then to 1180 in 1916.[204][208][211] |
| Arcturus (Alpha Bootis) |
Star | 1891 − 1910 | 160 ly (18 mas) (this is very inaccurate, true=37 ly) |
This number is wrong; originally announced in 1891, the figure was corrected in 1910 to 40 ly (60 mas). From 1891 to 1910, it had been thought this was the star with the smallest known parallax, hence the most distant star whose distance was known. Prior to 1891, Arcturus had previously been recorded of having a parallax of 127 mas.[212][213][214][215] |
| Capella (Alpha Aurigae) |
Star | 1849–1891 | 72 ly (46 mas) |
[216][217][218] |
| Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris) |
Star | 1847 – 1849 | 50 ly (80 mas) (this is very inaccurate, true=~375 ly) |
[219][220] |
| Vega (Alpha Lyrae) |
Star (part of a double star pair) | 1839 – 1847 | 7.77 pc (125 mas) |
[219] |
| 61 Cygni | Binary star | 1838 − 1839 | 3.48 pc (313.6 mas) |
This was the first star other than the Sun to have its distance measured.[219][221][222] |
| Uranus | Planet of the Solar System | 1781 − 1838 | 18 AU | This was the last planet discovered before the first successful measurement of stellar parallax. It had been determined that the stars were much farther away than the planets. |
| Saturn | Planet of the Solar System | 1619 − 1781 | 10 AU | From Kepler's Third Law, it was finally determined that Saturn is indeed the outermost of the classical planets, and its distance derived. It had only previously been conjectured to be the outermost, due to it having the longest orbital period, and slowest orbital motion. It had been determined that the stars were much farther away than the planets. |
| Mars | Planet of the Solar System | 1609 − 1619 | 2.6 AU when Mars is diametrically opposed to Earth | Kepler correctly characterized Mars and Earth's orbits in the publication Astronomia nova. It had been conjectured that the fixed stars were much farther away than the planets. |
| Sun | Star | 3rd century BC — 1609 | 380 Earth radii (very inaccurate, true=16000 Earth radii) | Aristarchus of Samos made a measurement of the distance of the Sun from the Earth in relation to the distance of the Moon from the Earth. The distance to the Moon was described in Earth radii (20, also inaccurate). The diameter of the Earth had been calculated previously. At the time, it was assumed that some of the planets were further away, but their distances could not be measured. The order of the planets was conjecture until Kepler determined the distances from the Sun of the five known planets that were not Earth. It had been conjectured that the fixed stars were much farther away than the planets. |
| Moon | Moon of a planet | 3rd century BC | 20 Earth radii (very inaccurate, true=64 Earth radii) | Aristarchus of Samos made a measurement of the distance between the Earth and the Moon. The diameter of the Earth had been calculated previously. |
List of objects by year of discovery that turned out to be most distant
[edit]This list contains a list of most distant objects by year of discovery of the object, not the determination of its distance. Objects may have been discovered without distance determination, and were found subsequently to be the most distant known at that time. However, object must have been named or described. An object like OJ 287 is ignored even though it was detected as early as 1891 using photographic plates, but ignored until the advent of radiotelescopes.
| Year of record | Modern light travel distance (Mly) |
Object | Type | Detected using | First record by (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 964 | 2.5[223] | Andromeda Galaxy | Spiral galaxy | naked eye | furthest object visible with the naked eye, but first recorded by Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi[224] |
| 1654 | 3 | Triangulum Galaxy | Spiral galaxy | refracting telescope | Giovanni Battista Hodierna[225] |
| 1779 | 68[226] | Messier 58 | Barred spiral galaxy | refracting telescope | Charles Messier[227] |
| 1785 | 76.4[228] | NGC 584 | Galaxy | William Herschel | |
| 1880s | 206 ± 29[229] | NGC 1 | Spiral galaxy | Dreyer, Herschel | |
| 1959 | 2,400[230] | 3C 273 | Quasar | Parkes Radio Telescope | Maarten Schmidt, Bev Oke[231] |
| 1960 | 5,000[232] | 3C 295 | Radio galaxy | Palomar Observatory | Rudolph Minkowski |
Data missing from table
| |||||
| 2009 | 13,000[233] | GRB 090423 | Gamma-ray burst progenitor | Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission | Krimm, H. et al.[234] |
See also
[edit]- Age of the universe
- List of largest cosmic structures
- List of exoplanet extremes
- Lists of astronomical objects
- List of most distant stars
- Timeline of knowledge about galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and large-scale structure
References
[edit]- ^ Planck Collaboration (2020). "Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 641. page A6 (see PDF page 15, Table 2: "Age/Gyr", last column). arXiv:1807.06209. Bibcode:2020A&A...641A...6P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833910. S2CID 119335614.
- ^ Guidry, Mike (2019). Modern general relativity: black holes, gravitational waves, and cosmology. Cambridge New York: Cambridge university press. ISBN 978-1-107-19789-3.
- ^ Davis, Tamara M.; Lineweaver, Charles H. (2004). "Expanding Confusion: Common Misconceptions of Cosmological Horizons and the Superluminal Expansion of the Universe". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia. 21 (1): 97–109. arXiv:astro-ph/0310808. Bibcode:2004PASA...21...97D. doi:10.1071/AS03040. ISSN 1323-3580. S2CID 13068122.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co "UCLA Cosmological Calculator". UCLA. 2015. Retrieved 6 August 2022. Light travel distance was calculated from redshift value using the UCLA Cosmological Calculator, with parameters values as of 2015: H0=67.74 and OmegaM=0.3089 (see Table/Planck2015 at "Lambda-CDM model#Parameters" )
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf "UCLA Cosmological Calculator". UCLA. 2018. Retrieved 6 August 2022. Light travel distance was calculated from redshift value using the UCLA Cosmological Calculator, with parameters values as of 2018: H0=67.4 and OmegaM=0.315 (see Table/Planck2018 at "Lambda-CDM model#Parameters" )
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce "ICRAR Cosmology Calculator". International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research. 2022. Retrieved 6 August 2022. ICRAR Cosmology Calculator - Set H0=67.4 and OmegaM=0.315 (see Table/Planck2018 at "Lambda-CDM model#Parameters")
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce Kempner, Joshua (2022). "KEMPNER Cosmology Calculator". Kempner.net. Retrieved 6 August 2022. KEMP Cosmology Calculator - Set H0=67.4, OmegaM=0.315, and OmegaΛ=0.6847 (see Table/Planck2018 at "Lambda-CDM model#Parameters")
- ^ a b Robertson, B.; et al. (2024-05-28). "Earliest galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: luminosity function and cosmic star-formation rate density 300 Myr after the Big Bang". Astrophysical Journal. 970 (1): 31. arXiv:2312.10033. Bibcode:2024ApJ...970...31R. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad463d.
- ^ Carniani, S.; et al. (2024-05-28). "A shining cosmic dawn: spectroscopic confirmation of two luminous galaxies at z ∼ 14". Astrophysical Journal. 633 (8029): 318–322. arXiv:2405.18485. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07860-9. PMC 11390484. PMID 39074505.
- ^ a b c d e Robertson, B. E.; et al. (2023). "Identification and properties of intense star-forming galaxies at redshifts z > 10". Nature Astronomy. 7 (5): 611–621. arXiv:2212.04480. Bibcode:2023NatAs...7..611R. doi:10.1038/s41550-023-01921-1. S2CID 257968812.
- ^ a b Wang, Bingjie; et al. (2023-11-13). "UNCOVER: Illuminating the Early Universe—JWST/NIRSpec Confirmation of z > 12 Galaxies". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 957 (2): L34. arXiv:2308.03745. Bibcode:2023ApJ...957L..34W. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acfe07. ISSN 2041-8205.
- ^ a b c Bunker, Andrew J.; et al. (2023). "JADES NIRSpec Spectroscopy of GN-z11: Lyman- α emission and possible enhanced nitrogen abundance in a z = 10.60 luminous galaxy". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 677: A88. arXiv:2302.07256. Bibcode:2023A&A...677A..88B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346159. S2CID 256846361.
- ^ Bakx, Tom J. L. C.; et al. (January 2023). "Deep ALMA redshift search of a z~12 GLASS-JWST galaxy candidate". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 519 (4): 5076–5085. arXiv:2208.13642. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3723.
- ^ Haro, Pablo Arrabal; Dickinson, Mark; Finkelstein, Steven L.; Kartaltepe, Jeyhan S.; Donnan, Callum T.; Burgarella, Denis; Carnall, Adam; Cullen, Fergus; Dunlop, James S.; Fernández, Vital; Fujimoto, Seiji; Jung, Intae; Krips, Melanie; Larson, Rebecca L.; Papovich, Casey (2023-08-14). "Confirmation and refutation of very luminous galaxies in the early universe". Nature. 622 (7984): 707–711. arXiv:2303.15431. Bibcode:2023Natur.622..707A. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06521-7. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 37579792. S2CID 257766818.
- ^ Harikane, Yuichi; Nakajima, Kimihiko; Ouchi, Masami; et al. (2023). "Pure Spectroscopic Constraints on UV Luminosity Functions and Cosmic Star Formation History From 25 Galaxies at $z_\mathrm{spec}=8.61-13.20$ Confirmed with JWST/NIRSpec". arXiv:2304.06658v3 [astro-ph.GA].
- ^ a b Oesch, P. A.; Brammer, G.; van Dokkum, P.; et al. (March 2016). "A Remarkably Luminous Galaxy at z=11.1 Measured with Hubble Space Telescope Grism Spectroscopy". The Astrophysical Journal. 819 (2). 129. arXiv:1603.00461. Bibcode:2016ApJ...819..129O. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/819/2/129. S2CID 119262750.
- ^ a b Jiang, Linhua; et al. (January 2021). "Evidence for GN-z11 as a luminous galaxy at redshift 10.957". Nature Astronomy. 5 (3): 256–261. arXiv:2012.06936. Bibcode:2021NatAs...5..256J. doi:10.1038/s41550-020-01275-y. S2CID 229156468.
- ^ Roberts-Borsani, Guido; Treu, Tommaso; Chen, Wenlei; Morishita, Takahiro; Vanzella, Eros; Zitrin, Adi; Bergamini, Pietro; Castellano, Marco; Fontana, Adriano; Grillo, Claudio; Kelly, Patrick L.; Merlin, Emiliano; Paris, Diego; Rosati, Piero; Acebron, Ana (2023). "A shot in the Dark (Ages): a faint galaxy at $z=9.76$ confirmed with JWST". Nature Astronomy. 618 (7965): 480–483. arXiv:2210.15639. Bibcode:2023Natur.618..480R. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-05994-w. PMID 37198479. S2CID 258741077.
- ^ Boyett, Kristan; Trenti, Michele; Leethochawalit, Nicha; Calabró, Antonello; Metha, Benjamin; Roberts-Borsani, Guido; Dalmasso, Nicoló; Yang, Lilan; Santini, Paola; Treu, Tommaso; Jones, Tucker; Henry, Alaina; Mason, Charlotte A.; Morishita, Takahiro; Nanayakkara, Themiya (2024-03-07). "A massive interacting galaxy 510 million years after the Big Bang". Nature Astronomy. 8 (5): 657–672. arXiv:2303.00306. Bibcode:2024NatAs...8..657B. doi:10.1038/s41550-024-02218-7. ISSN 2397-3366.
- ^ T. Hashimoto; N. Laporte; K. Mawatari; R. S. Ellis; A. K. Inoue; E. Zackrisson; G. Roberts-Borsani; W. Zheng; Y. Tamura; F. E. Bauer; T. Fletcher; Y. Harikane; B. Hatsukade; N. H. Hayatsu; Y. Matsuda; H. Matsuo; T. Okamoto; M. Ouchi; R. Pello; C. Rydberg; I. Shimizu; Y. Taniguchi; H. Umehata; N. Yoshida (2019). "The Onset of Star Formation 250 Million Years After the Big Bang". Nature. 557 (7705): 312–313. arXiv:1805.05966. Bibcode:2018Natur.557..392H. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0117-z. PMID 29765123. S2CID 21702406.
- ^ Adi Zitrin; Ivo Labbe; Sirio Belli; Rychard Bouwens; Richard S. Ellis; Guido Roberts-Borsani; Daniel P. Stark; Pascal A. Oesch; Renske Smit (2015). "Lyman-alpha Emission from a Luminous z = 8.68 Galaxy: Implications for Galaxies as Tracers of Cosmic Reionization". The Astrophysical Journal. 810 (1): L12. arXiv:1507.02679. Bibcode:2015ApJ...810L..12Z. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/810/1/L12. S2CID 11524667.
- ^ a b c Curti, Mirko; et al. (January 2023). "The chemical enrichment in the early Universe as probed by JWST via direct metallicity measurements at z 8". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 518 (1): 425–438. arXiv:2207.12375. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.518..425C. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2737.
- ^ a b c Carnall, A. C.; et al. (January 2023). "A first look at the SMACS0723 JWST ERO: spectroscopic redshifts, stellar masses, and star-formation histories". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters. 518 (1): L45 – L50. arXiv:2207.08778. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.518L..45C. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slac136.
- ^ a b c Schaerer, D.; et al. (September 2022). "First look with JWST spectroscopy: Resemblance among z ~ 8 galaxies and local analogs". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 665: 6. arXiv:2207.10034. Bibcode:2022A&A...665L...4S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202244556. S2CID 252175886. L4.
- ^ a b c Katz, Harley; et al. (January 2023). "First insights into the ISM at z > 8 with JWST: possible physical implications of a high [O III] λ4363/[O III] λ5007". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 518 (1): 592–603. arXiv:2207.13693. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.518..592K. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2657.
- ^ Laporte, N.; Ellis, R. S.; Boone, F.; Bauer, F. E.; Quénard, D.; Roberts-Borsani, G. W.; Pelló, R.; Pérez-Fournon, I.; Streblyanska, A. (2017). "Dust in the Reionization Era: ALMA Observations of a z = 8.38 Gravitationally Lensed Galaxy". The Astrophysical Journal. 832 (2): L21. arXiv:1703.02039. Bibcode:2017ApJ...837L..21L. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa62aa. S2CID 51841290.
- ^ Tamura, Y.; Mawatari, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Inoue, A. K.; Zackrisson, E.; Christensen, L.; Binggeli, C; Matsuda, Y.; Matsuo, H.; Takeuchi, T. T.; Asano, R. S.; Sunaga, K.; Shimizu, I.; Okamoto, T.; Yoshida, N.; Lee, M.; Shibuya, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Umehata, H.; Hatsukade, B.; Kohno, K.; Ota, K. (2017). "Detection of the Far-infrared [O III] and Dust Emission in a Galaxy at Redshift 8.312: Early Metal Enrichment in the Heart of the Reionization Era". The Astrophysical Journal. 874 (1): 27. arXiv:1806.04132. Bibcode:2019ApJ...874...27T. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab0374. S2CID 55313459.
- ^ a b c d Tanvir, N. R.; Fox, D. B.; Levan, A. J.; Berger, E.; Wiersema, K.; Fynbo, J. P. U.; Cucchiara, A.; Krühler, T.; Gehrels, N.; Bloom, J. S.; Greiner, J.; Evans, P. A.; Rol, E.; Olivares, F.; Hjorth, J.; Jakobsson, P.; Farihi, J.; Willingale, R.; Starling, R. L. C.; Cenko, S. B.; Perley, D.; Maund, J. R.; Duke, J.; Wijers, R. A. M. J.; Adamson, A. J.; Allan, A.; Bremer, M. N.; Burrows, D. N.; Castro-Tirado, A. J.; et al. (2009). "A gamma-ray burst at a redshift of z~8.2". Nature. 461 (7268): 1254–7. arXiv:0906.1577. Bibcode:2009Natur.461.1254T. doi:10.1038/nature08459. PMID 19865165. S2CID 205218350.
- ^ a b Langeroodi, Danial; Hjorth, Jens; Chen, Wenlei; Kelly, Patrick L.; Williams, Hayley; Lin, Yu-Heng; Scarlata, Claudia; Zitrin, Adi; Broadhurst, Tom; Diego, Jose M.; Huang, Xiaosheng; Filippenko, Alexei V.; Foley, Ryan J.; Jha, Saurabh; Koekemoer, Anton M.; Oguri, Masamune; Perez-Fournon, Ismael; Pierel, Justin; Poidevin, Frederick; Strolger, Lou (2022). "Evolution of the Mass-Metallicity Relation from Redshift z≈8 to the Local Universe". The Astrophysical Journal. 804 (2). arXiv:2212.02491. Bibcode:2015ApJ...804L..30O. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/804/2/L30. S2CID 55115344.
- ^ P. A. Oesch; P. G. van Dokkum; G. D. Illingworth; R. J. Bouwens; I. Momcheva; B. Holden; G. W. Roberts-Borsani; R. Smit; M. Franx; I. Labbe; V. Gonzalez; D. Magee (2015). "A Spectroscopic Redshift Measurement for a Luminous Lyman Break Galaxy at z = 7.730 using Keck/MOSFIRE". The Astrophysical Journal. 804 (2): L30. arXiv:1502.05399. Bibcode:2015ApJ...804L..30O. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/804/2/L30. S2CID 55115344.
- ^ Song, M.; Finkelstein, S. L.; Livermore, R. C.; Capak, P. L.; Dickinson, M.; Fontana, A. (2016). "Keck/MOSFIRE Spectroscopy of z = 7–8 Galaxies: Lyman-alpha Emission from a Galaxy at z = 7.66". The Astrophysical Journal. 826 (2): 113. arXiv:1602.02160. Bibcode:2016ApJ...826..113S. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/826/2/113. S2CID 51806693.
- ^ Wang, Feige; Yang, Jinyi; Fan, Xiaohui; Hennawi, Joseph F.; Barth, Aaron J.; Banados, Eduardo; Bian, Fuyan; Boutsia, Konstantina; Connor, Thomas; Davies, Frederick B.; Decarli, Roberto; Eilers, Anna-Christina; Farina, Emanuele Paolo; Green, Richard; Jiang, Linhua; Li, Jiang-Tao; Mazzucchelli, Chiara; Nanni, Riccardo; Schindler, Jan-Torge; Venemans, Bram; Walter, Fabian; Wu, Xue-Bing; Yue, Minghao (2021). "A Luminous Quasar at Redshift 7.642". The Astrophysical Journal. 907 (1): L1. arXiv:2101.03179. Bibcode:2021ApJ...907L...1W. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abd8c6. S2CID 231572944.
- ^ Bañados, Eduardo; et al. (6 December 2017). "An 800-million-solar-mass black hole in a significantly neutral Universe at a redshift of 7.5". Nature. 553 (7689): 473–476. arXiv:1712.01860. Bibcode:2018Natur.553..473B. doi:10.1038/nature25180. PMID 29211709. S2CID 205263326.
- ^ S. L. Finkelstein; C. Papovich; M. Dickinson; M. Song; V. Tilvi; A. M. Koekemoer; K. D. Finkelstein; B. Mobasher; H. C. Ferguson; M. Giavalisco; N. Reddy; M. L. N. Ashby; A. Dekel; G. G. Fazio; A. Fontana; N. A. Grogin; J.-S. Huang; D. Kocevski; M. Rafelski; B. J. Weiner; S. P. Willner (2013). "A galaxy rapidly forming stars 700 million years after the Big Bang at redshift 7.51". Nature. 502 (7472): 524–527. arXiv:1310.6031. Bibcode:2013Natur.502..524F. doi:10.1038/nature12657. PMID 24153304. S2CID 4448085.
- ^ Watson, Darach; Christensen, Lise; Knudsen, Kirsten Kraiberg; Richard, Johan; Gallazzi, Anna; Michałowski, Michał Jerzy (2015). "A dusty, normal galaxy in the epoch of reionization". Nature. 519 (7543): 327–330. arXiv:1503.00002. Bibcode:2015Natur.519..327W. doi:10.1038/nature14164. PMID 25731171. S2CID 2514879.
- ^ Larson, R. L.; Finkelstein, S. L.; Pirzkal, N.; Ryan, R.; Tilvi, V.; Malhotra, S.; Rhoads, J.; Finkelstein, K.; Jung, I.; Christensen, L.; Cimatti, A.; Ferreras, I.; Grogin, N.; Koekemoer, A. M.; Hathi, N.; O'Connell, R.; Östlin, G.; Pasquali, A.; Pharo, J.; Rothberg, B.; Windhorst, R. A. (2018). "Discovery of a z = 7.452 High Equivalent Width Lyman alpha Emitter from the Hubble Space Telescope Faint Infrared Grism Survey". The Astrophysical Journal. 858 (2): 113. arXiv:1712.05807. Bibcode:2018ApJ...858...94L. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aab893. S2CID 119257857.
- ^ a b c Ono, Yoshiaki; Ouchi, Masami; Mobasher, Bahram; Dickinson, Mark; Penner, Kyle; Shimasaku, Kazuhiro; Weiner, Benjamin J.; Kartaltepe, Jeyhan S.; Nakajima, Kimihiko; Nayyeri, Hooshang; Stern, Daniel; Kashikawa, Nobunari; Spinrad, Hyron (2011). "Spectroscopic Confirmation of Three z-Dropout Galaxies at z = 6.844 – 7.213: Demographics of Lyman-Alpha Emission in z ~ 7 Galaxies". The Astrophysical Journal. 744 (2): 83. arXiv:1107.3159. Bibcode:2012ApJ...744...83O. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/744/2/83. S2CID 119306980.
- ^ Inoue, Akio K.; et al. (June 2016). "Detection of an oxygen emission line from a high redshift galaxy in the reionization epoch" (PDF). Science. 352 (6293): 1559–1562. arXiv:1606.04989. Bibcode:2016Sci...352.1559I. doi:10.1126/science.aaf0714. PMID 27312046. S2CID 206646433.
- ^ a b Vanzella; et al. (2011). "Spectroscopic Confirmation of Two Lyman Break Galaxies at Redshift Beyond 7". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 730 (2): L35. arXiv:1011.5500. Bibcode:2011ApJ...730L..35V. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/730/2/L35. S2CID 53459241.
- ^ Daniel J. Mortlock; Stephen J. Warren; Bram P. Venemans; et al. (2011). "A luminous quasar at a redshift of z = 7.085". Nature. 474 (7353): 616–619. arXiv:1106.6088. Bibcode:2011Natur.474..616M. doi:10.1038/nature10159. PMID 21720366. S2CID 2144362.
- ^ Schenker, Matthew A.; et al. (January 2012). "Keck Spectroscopy of Faint 3 < z < 8 Lyman Break Galaxies: Evidence for a Declining Fraction of Emission Line Sources in the Redshift Range 6 < z < 8". The Astrophysical Journal. 744 (2): 7. arXiv:1107.1261. Bibcode:2012ApJ...744..179S. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/744/2/179. S2CID 119244384.
- ^ Fontana, A.; Vanzella, E.; Pentericci, L.; Castellano, M.; Giavalisco, M.; Grazian, A.; Boutsia, K.; Cristiani, S.; Dickinson, M.; Giallongo, E.; Maiolino, M.; Moorwood, A.; Santini, P. (2010). "The lack of intense Lyman~alpha in ultradeep spectra of z = 7 candidates in GOODS-S: Imprint of reionization?". The Astrophysical Journal. 725 (2): L205. arXiv:1010.2754. Bibcode:2010ApJ...725L.205F. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/725/2/L205. S2CID 119270473.
- ^ Rhoads, James E.; Hibon, Pascale; Malhotra, Sangeeta; Cooper, Michael; Weiner, Benjamin (2012). "A Lyman Alpha Galaxy at Redshift z = 6.944 in the COSMOS Field". The Astrophysical Journal. 752 (2): L28. arXiv:1205.3161. Bibcode:2012ApJ...752L..28R. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/752/2/L28. S2CID 118383532.
- ^ Bañados, Eduardo; Mazzucchelli, Chiara; Momjian, Emmanuel; Eilers, Anna-Christina; Wang, Feige; Schindler, Jan-Torge; Connor, Thomas; Andika, Irham Taufik; Barth, Aaron J.; Carilli, Chris; Davies, Frederick B.; Decarli, Roberto; Fan, Xiaohui; Farina, Emanuele Paolo; Hennawi, Joseph F.; Pensabene, Antonio; Stern, Daniel; Venemans, Bram P.; Wenzl, Lukas; Yang, Jinyi (2021). "The Discovery of a Highly Accreting, Radio-loud Quasar at z = 6.82". The Astrophysical Journal. 909 (1). Harvard University: 80. arXiv:2103.03295. Bibcode:2021ApJ...909...80B. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abe239. S2CID 232135300.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac Adams, N. J.; et al. (November 2022). "Discovery and properties of ultra-high redshift galaxies (9 < z < 12) in the JWST ERO SMACS 0723 Field". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 518 (3): 4755–4766. arXiv:2207.11217. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.518.4755A. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3347.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar Yan, Haojing; et al. (January 2023). "First Batch of z ≈ 11–20 Candidate Objects Revealed by the James Webb Space Telescope Early Release Observations on SMACS 0723-73". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 942 (L9): 20. arXiv:2207.11558. Bibcode:2023ApJ...942L...9Y. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aca80c.
- ^ Garth Illingworth; Rychard Bouwens; Pascal Oesch; Ivo Labbe; Dan Magee (December 2012). "Our Latest Results". FirstGalaxies. Retrieved March 10, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Harikane, Yuichi; et al. (2023). "A Comprehensive Study of Galaxies at z ~ 9–16 Found in the Early JWST Data: Ultraviolet Luminosity Functions and Cosmic Star Formation History at the Pre-reionization Epoch". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 265 (1): 5. arXiv:2208.01612. Bibcode:2023ApJS..265....5H. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/acaaa9. S2CID 251253150.
- ^ a b Fujimoto, Seiji; et al. (2023). "ALMA FIR View of Ultra High-redshift Galaxy Candidates at z ~ 11-17: Blue Monsters or Low- z Red Interlopers?". The Astrophysical Journal. 955 (2): 130. arXiv:2211.03896. Bibcode:2023ApJ...955..130F. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aceb67.
- ^ a b Morishita, Takahiro; Stiavelli, Massimo (2023). "Physical Characterization of Early Galaxies in the Webb's First Deep Field SMACS J0723.3-7323". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 946 (2): L35. arXiv:2207.11671v2. Bibcode:2023ApJ...946L..35M. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acbf50. S2CID 254220684.
- ^ Harikane, Yuichi; Ouchi, Masami; Oguri, Masamune; Ono, Yoshiaki; Nakajima, Kimihiko; Isobe, Yuki; Umeda, Hiroya; Mawatari, Ken; Zhang, Yechi (2023). "A Comprehensive Study of Galaxies at z ~ 9–16 Found in the Early JWST Data: Ultraviolet Luminosity Functions and Cosmic Star Formation History at the Pre-reionization Epoch". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 265 (1): 5. arXiv:2208.01612v3. Bibcode:2023ApJS..265....5H. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/acaaa9. S2CID 251253150.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Hakim, Atek; et al. (November 2022). "Revealing galaxy candidates out to z 16 with JWST observations of the lensing cluster SMACS0723". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 519 (1): 1201–1220. arXiv:2207.12338. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.519.1201A. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3144.
- ^ Harikane, Y.; et al. (April 2022). "A Search for H-Dropout Lyman Break Galaxies at z ~ 12–16". The Astrophysical Journal. 929 (1): 1. arXiv:2112.09141. Bibcode:2022ApJ...929....1H. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac53a9. S2CID 246823511.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Donnan, C. T.; et al. (November 2022). "The evolution of the galaxy UV luminosity function at redshifts z ≃ 8 - 15 from deep JWST and ground-based near-infrared imaging". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 518 (4): 6011–6040. arXiv:2207.12356. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.518.6011D. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3472.
- ^ a b c Bouwens, Rychard J.; et al. (2023). "Evolution of the UV LF from z ~ 15 to z ~ 8 using new JWST NIRCam medium-band observations over the HUDF/XDF". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 523: 1036–1055. arXiv:2211.02607. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad1145.
- ^ Rodighiero, Giulia; et al. (January 2023). "JWST unveils heavily obscured (active and passive) sources up to z 13". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters. 518 (1): L19 – L24. arXiv:2208.02825. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.518L..19R. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slac115.
- ^ a b Whitler, Lily; et al. (December 2022). "On the ages of bright galaxies 500 Myr after the Big Bang: insights into star formation activity at z ≳ 15 with JWST". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 519 (1): 157–171. arXiv:2208.01599. Bibcode:2023MNRAS.519..157W. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3535.
- ^ Coe, Dan; Zitrin, Adi; Carrasco, Mauricio; Shu, Xinwen; Zheng, Wei; Postman, Marc; Bradley, Larry; Koekemoer, Anton; Bouwens, Rychard; Broadhurst, Tom; Monna, Anna; Host, Ole; Moustakas, Leonidas A.; Ford, Holland; Moustakas, John; Van Der Wel, Arjen; Donahue, Megan; Rodney, Steven A.; Benítez, Narciso; Jouvel, Stephanie; Seitz, Stella; Kelson, Daniel D.; Rosati, Piero (2013). "CLASH: Three Strongly Lensed Images of a Candidate z ~ 11 Galaxy". The Astrophysical Journal. 762 (1): 32. arXiv:1211.3663. Bibcode:2013ApJ...762...32C. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/762/1/32. S2CID 119114237.
- ^ Hsiao, Tiger Yu-Yang; et al. (2023). "JWST Reveals a Possible z ~ 11 Galaxy Merger in Triply Lensed MACS0647–JD". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 949 (2): L34. arXiv:2210.14123. Bibcode:2023ApJ...949L..34H. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acc94b. S2CID 253107903.
- ^ Naidu, Rohan P.; et al. (November 2022). "Two Remarkably Luminous Galaxy Candidates at z ≈ 10 − 12 Revealed by JWST". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 940 (1): 11. arXiv:2207.09434. Bibcode:2022ApJ...940L..14N. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac9b22. S2CID 250644267. L14.
- ^ Yoon, Ilsang; et al. (2023). "ALMA Observation of a z ≳ 10 Galaxy Candidate Discovered with JWST". The Astrophysical Journal. 950 (1): 61. arXiv:2210.08413. Bibcode:2023ApJ...950...61Y. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acc94d.
- ^ Salmon, Brett; Coe, Dan; Bradley, Larry; Bradač, Marusa; Huang, Kuang-Han; Strait, Victoria; Oesch, Pascal; Paterno-Mahler, Rachel; Zitrin, Adi; Acebron, Ana; Cibirka, Nathália; Kikuchihara, Shotaro; Oguri, Masamune; Brammer, Gabriel B; Sharon, Keren; Trenti, Michele; Avila, Roberto J; Ogaz, Sara; Andrade-Santos, Felipe; Carrasco, Daniela; Cerny, Catherine; Dawson, William; Frye, Brenda L; Hoag, Austin; Jones, Christine; Mainali, Ramesh; Ouchi, Masami; Rodney, Steven A; Stark, Daniel; Umetsu, Keiichi (2018). "A Candidate z~10 Galaxy Strongly Lensed into a Spatially Resolved Arc". The Astrophysical Journal. 864: L22. arXiv:1801.03103. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aadc10. S2CID 78087820.
- ^ "Hubble Finds Distant Galaxy Through Cosmic Magnifying Glass". NASA. 23 April 2015.
- ^ Zitrin, Adi; Zheng, Wei; Broadhurst, Tom; Moustakas, John; Lam, Daniel; Shu, Xinwen; Huang, Xingxing; Diego, Jose M.; Ford, Holland; Lim, Jeremy; Bauer, Franz E.; Infante, Leopoldo; Kelson, Daniel D.; Molino, Alberto (2014). "A Geometrically Supported z ~ 10 Candidate Multiply Imaged by the Hubble Frontier Fields Cluster A2744" (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal. 793 (1): L12. arXiv:1407.3769. Bibcode:2014ApJ...793L..12Z. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/793/1/L12. S2CID 43853349.
- ^ "NASA Telescopes Spy Ultra-Distant Galaxy". NASA.
- ^ Zheng, W.; Postman, M.; Zitrin, A.; Moustakas, J.; Shu, X.; Jouvel, S.; Høst, O.; Molino, A.; Bradley, L.; Coe, D.; Moustakas, L. A.; Carrasco, M.; Ford, H.; Benítez, N.; Lauer, T. R.; Seitz, S.; Bouwens, R.; Koekemoer, A.; Medezinski, E.; Bartelmann, M.; Broadhurst, T.; Donahue, M.; Grillo, C.; Infante, L.; Jha, S. W.; Kelson, D. D.; Lahav, O.; Lemze, D.; Melchior, P.; Meneghetti, M. (2012). "A magnified young galaxy from about 500 million years after the Big Bang". Nature. 489 (7416): 406–408. arXiv:1204.2305. Bibcode:2012Natur.489..406Z. doi:10.1038/nature11446. PMID 22996554. S2CID 4415218.
- ^ Penn State Science, "Cosmic Explosion is New Candidate for Most Distant Object in the Universe", Derek. B. Fox, Barbara K. Kennedy, 25 May 2011
- ^ Space Daily, Explosion Helps Researcher Spot Universe's Most Distant Object, 27 May 2011
- ^ "ESA Science & Technology: The Hubble eXtreme Deep Field (annotated)".
- ^ David Shiga. "Dim galaxy is most distant object yet found". New Scientist.
- ^ Bunker, Andrew J.; Caruana, Joseph; Wilkins, Stephen M.; Stanway, Elizabeth R.; Lorenzoni, Silvio; Lacy, Mark; Jarvis, Matt J.; Hickey, Samantha (2013). "VLT/XSHOOTER and Subaru/MOIRCS spectroscopy of HUDF.YD3: no evidence for Lyman &". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 430 (4): 3314. arXiv:1301.4477. Bibcode:2013MNRAS.430.3314B. doi:10.1093/mnras/stt132.
- ^ Trenti, M.; Bradley, L. D.; Stiavelli, M.; Shull, J. M.; Oesch, P.; Bouwens, R. J.; Munoz, J. A.; Romano-Diaz, E.; Treu, T.; Shlosman, I.; Carollo, C. M. (2011). "Overdensities of Y-dropout Galaxies from the Brightest-of-Reionizing Galaxies Survey: A Candidate Protocluster at Redshift z ≈ 8". The Astrophysical Journal. 746 (1): 55. arXiv:1110.0468. Bibcode:2012ApJ...746...55T. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/746/1/55. S2CID 119294290.
- ^ Wang, Tao; Elbaz, David; Daddi, Emanuele; Finoguenov, Alexis; Liu, Daizhong; Schrieber, Corenin; Martin, Sergio; Strazzullo, Veronica; Valentino, Francesco; van Der Burg, Remco; Zanella, Anita; Cisela, Laure; Gobat, Raphael; Le Brun, Amandine; Pannella, Maurilio; Sargent, Mark; Shu, Xinwen; Tan, Qinghua; Cappelluti, Nico; Li, Xanxia (2016). "Discovery of a galaxy cluster with a violently starbursting core at z=2.506". The Astrophysical Journal. 828 (1): 56. arXiv:1604.07404. Bibcode:2016ApJ...828...56W. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/828/1/56. S2CID 8771287.
- ^ Cucciati, O.; Lemaux, B. C.; Zamorani, G.; Le Fevre, O.; Tasca, L. A. M.; Hathi, N. P.; Lee, K-G.; Bardelli, S.; Cassata, P.; Garilli, B.; Le Brun, V.; Maccagni, D.; Pentericci, L.; Thomas, R.; Vanzella, E.; Zucca, E.; Lubin, L. M.; Amorin, R.; Cassara', L. P.; Cimatti, A.; Talia, M.; Vergani, D.; Koekemoer, A.; Pforr, J.; Salvato, M. (2018). "The progeny of a Cosmic Titan: a massive multi-component proto-supercluster in formation at z=2.45 in VUDS". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 619: A49. arXiv:1806.06073. Bibcode:2018A&A...619A..49C. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833655. S2CID 119472428.
- ^ Morishita, Takahiro; Roberts-Borsani, Guido; Treu, Tommaso; Brammer, Gabriel; Mason, Charlotte A.; Trenti, Michele; Vulcani, Benedetta; Wang, Xin; Acebron, Ana; Bahé, Yannick; Bergamini, Pietro; Boyett, Kristan; Bradac, Marusa; Calabrò, Antonello; Castellano, Marco; Chen, Wenlei; De Lucia, Gabriella; Filippenko, Alexei V.; Fontana, Adriano; Glazebrook, Karl; Grillo, Claudio; Henry, Alaina; Jones, Tucker; Kelly, Patrick L.; Koekemoer, Anton M.; Leethochawalit, Nicha; Lu, Ting-Yi; Marchesini, Danilo; Mascia, Sara; Mercurio, Amata; Merlin, Emiliano; Metha, Benjamin; Nanayakkara, Themiya; Nonino, Mario; Paris, Diego; Pentericci, Laura; Santini, Paola; Strait, Victoria; Vanzella, Eros; Windhorst, Rogier A.; Rosati, Piero; Xie, Lizhi (30 January 2023). "Early results from GLASS-JWST. XVIII: A spectroscopically confirmed protocluster 650 million years after the Big Bang". Astrophysical Journal Letters. 947 (2). arXiv:2211.09097. Bibcode:2023ApJ...947L..24M. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acb99e. S2CID 253553396.
- ^ Bogdán, Ákos; et al. (2023-11-06), "Evidence for heavy-seed origin of early supermassive black holes from a z ≈ 10 X-ray quasar", Nature Astronomy, 8 (1): 126–133, arXiv:2305.15458, Bibcode:2024NatAs...8..126B, doi:10.1038/s41550-023-02111-9, S2CID 258887541, retrieved 2024-08-31
- ^ Bunker, Andrew J.; et al. (2023). "JADES NIRSpec Spectroscopy of GN-z11: Lyman- α emission and possible enhanced nitrogen abundance in a z = 10.60 luminous galaxy". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 677: A88. arXiv:2302.07256. Bibcode:2023A&A...677A..88B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346159.
- ^ Robert Lea (January 17, 2024). "James Webb Space Telescope discovers oldest and most distant black hole ever seen". Space.com.
- ^ Joe Pinkstone (January 17, 2024). "Oldest black hole ever seen challenges what we know about their formation". The Telegraph.
- ^ Maiolino, Roberto; Scholtz, Jan; Witstok, Joris; Carniani, Stefano; D'Eugenio, Francesco; de Graaff, Anna; Übler, Hannah; Tacchella, Sandro; Curtis-Lake, Emma; Arribas, Santiago; Bunker, Andrew; Charlot, Stéphane; Chevallard, Jacopo; Curti, Mirko; Looser, Tobias J.; Maseda, Michael V.; Rawle, Timothy D.; Rodríguez del Pino, Bruno; Willott, Chris J.; Egami, Eiichi; Eisenstein, Daniel J.; Hainline, Kevin N.; Robertson, Brant; Williams, Christina C.; Willmer, Christopher N. A.; Baker, William M.; Boyett, Kristan; DeCoursey, Christa; Fabian, Andrew C.; Helton, Jakob M.; Ji, Zhiyuan; Jones, Gareth C.; Kumari, Nimisha; Laporte, Nicolas; Nelson, Erica J.; Perna, Michele; Sandles, Lester; Shivaei, Irene; Sun, Fengwu (17 January 2024). "A small and vigorous black hole in the early Universe". Nature. 627 (8002): 59–63. arXiv:2305.12492. Bibcode:2024Natur.627...59M. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07052-5. PMID 38232944. Retrieved 4 March 2024.
- ^ a b NASA, "New Gamma-Ray Burst Smashes Cosmic Distance Record" Archived 2011-03-10 at the Wayback Machine, 28 April 2009
- ^ a b Science Codex, "GRB 090429B – most distant gamma-ray burst yet" Archived 2011-05-31 at the Wayback Machine, NASA/Goddard, 27 May 2011
- ^ Welch, Brian; et al. (30 March 2022). "A highly magnified star at redshift 6.2". Nature. 603 (7903): 815–818. arXiv:2209.14866. Bibcode:2022Natur.603..815W. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04449-y. PMID 35354998. S2CID 247842625. Retrieved 30 March 2022.
- ^ Gianopoulos, Andrea (30 March 2022). "Record Broken: Hubble Spots Farthest Star Ever Seen". NASA. Retrieved 30 March 2022.
- ^ Camille M. Carlisle (12 April 2013). "The Most Distant Star Ever Seen?". Sky and Telescope.
- ^ Kelly, Patrick L.; et al. (2018). "Extreme magnification of an individual star at redshift 1.5 by a galaxy-cluster lens". Nature Astronomy. 2 (4): 334–342. arXiv:1706.10279. Bibcode:2018NatAs...2..334K. doi:10.1038/s41550-018-0430-3. S2CID 119412560.
- ^ Mowla, Lamiya; et al. (October 2022). "The Sparkler: Evolved High-redshift Globular Cluster Candidates Captured by JWST". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 937 (2): 9. arXiv:2208.02233. Bibcode:2022ApJ...937L..35M. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac90ca. L35.
- ^ Connor, Thomas; Bañados, Eduardo; Stern, Daniel; Carilli, Chris; Fabian, Andrew; Momjian, Emmanuel; Rojas-Ruiz, Sofía; Decarli, Roberto; Farina, Emanuele Paolo; Mazzucchelli, Chiara; Earnshaw, Hannah P. (2021). "Enhanced X-Ray Emission from the Most Radio-powerful Quasar in the Universe's First Billion Years". The Astrophysical Journal. 911 (2): 120. arXiv:2103.03879. Bibcode:2021ApJ...911..120C. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abe710. S2CID 232148026.
- ^ NASA.gov
- ^ SpaceDaily, "Record-Setting X-ray Jet Discovered", 30 November 2012 (accessed 4 December 2012)
- ^ ESA, "Artist's impression of the X-ray binary XMMU J004243.6+412519", 12 December 2012 (accessed 18 December 2012)
- ^ e! Science News, "XMMU J004243.6+412519: Black-Hole Binary At The Eddington Limit", 12 December 2012 (accessed 18 December 2012)
- ^ SpaceDaily, "Microquasar found in neighbor galaxy, tantalizing scientists", 17 December 2012 (accessed 18 December 2012)
- ^ Ouchi, Masami; Ono, Yoshiaki; Egami, Eiichi; Saito, Tomoki; Oguri, Masamune; McCarthy, Patrick J.; Farrah, Duncan; Kashikawa, Nobunari; Momcheva, Ivelina; Shimasaku, Kazuhiro; Nakanishi, Kouichiro; Furusawa, Hisanori; Akiyama, Masayuki; Dunlop, James S.; Mortier, Angela M. J. (2009-05-01). "Discovery of a Giant Lyα Emitter Near the Reionization Epoch". The Astrophysical Journal. 696 (2): 1164–1175. arXiv:0807.4174. Bibcode:2009ApJ...696.1164O. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/696/2/1164. ISSN 0004-637X. S2CID 15246638.
- ^ Hsu, Jeremy (2009-04-22). "Giant Mystery Blob Discovered Near Dawn of Time". SPACE.com. Retrieved 2009-04-24.
- ^ USA Today, "Smallest, most distant planet outside solar system found", Malcolm Ritter, 25 January 2006 (accessed 5 August 2010)
- ^ Schneider, J. "Notes for star PA-99-N2". Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. Archived from the original on February 6, 2010. Retrieved 2010-08-06.
- ^ Exoplaneten.de, "The Microlensing Event of Q0957+561" Archived 2012-02-11 at the Wayback Machine (accessed 5 August 2010)
- ^ Schild, R.E. (1996). "Microlensing Variability of the Gravitationally Lensed Quasar Q0957+561 A, B". Astrophysical Journal. 464: 125. Bibcode:1996ApJ...464..125S. doi:10.1086/177304.
- ^ Cooke, Jeff; Sullivan, Mark; Gal-Yam, Avishay; Barton, Elizabeth J.; Carlberg, Raymond G.; Ryan-Weber, Emma V.; Horst, Chuck; Omori, Yuuki; Díaz, C. Gonzalo (2012). "Superluminous supernovae at redshifts of 2.05 and 3.90". Nature. 491 (7423): 228–31. arXiv:1211.2003. Bibcode:2012Natur.491..228C. doi:10.1038/nature11521. PMID 23123848. S2CID 4397580.
- ^ "Record-breaking supernova in the CANDELS Ultra Deep Survey: before, after, and difference". www.spacetelescope.org.
- ^ Science Newsline, "The Farthest Supernova Yet for Measuring Cosmic History" Archived 2013-05-21 at the Wayback Machine, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 9 January 2013 (accessed 10 January 2013)
- ^ Mike Wall, "Most Distant 'Standard Candle' Star Explosion Found", Space.com, 9 January 2013 (accessed 10 January 2013)
- ^ Hinshaw, G.; Weiland, J. L.; Hill, R. S.; Odegard, N.; Larson, D.; Bennett, C. L.; Dunkley, J.; Gold, B.; Greason, M. R.; Jarosik, N.; Komatsu, E.; Nolta, M. R.; Page, L.; Spergel, D. N.; Wollack, E.; Halpern, M.; Kogut, A.; Limon, M.; Meyer, S. S.; Tucker, G. S.; Wright, E. L. (2009). "Five-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe Observations: Data Processing, Sky Maps, and Basic Results". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 180 (2): 225–245. arXiv:0803.0732. Bibcode:2009ApJS..180..225H. doi:10.1088/0067-0049/180/2/225. S2CID 3629998.
- ^ Redshift states the Cosmic microwave background radiation as having a redshift of z = 1089
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (3 March 2016). "Hubble sets new cosmic distance record". BBC News.
- ^ Wall, Mike (5 August 2015). "Ancient Galaxy Is Most Distant Ever Found". Space.com.
- ^ W. M. Keck Observatory (6 August 2015). "A new record: Keck Observatory measures most distant galaxy". Astronomy Now.
- ^ Mario De Leo Winkler (15 July 2015). "The Farthest Object in the Universe". Huffington Post.
- ^ a b Courtland, Rachel (27 April 2009). "Most distant object in the universe spotted". New Scientist. Retrieved 2009-11-11.
- ^ Shiga, David (13 September 2006). "First generation of galaxies glimpsed forming". New Scientist. Retrieved 2009-11-11.
- ^ Iye, M.; Ota, K.; Kashikawa, N.; Furusawa, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Hattori, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Morokuma, T.; Ouchi, M.; Shimasaku, K. (2006). "A galaxy at a redshift z = 6.96". Nature. 443 (7108): 186–188. arXiv:astro-ph/0609393. Bibcode:2006Natur.443..186I. doi:10.1038/nature05104. PMID 16971942. S2CID 2876103.
- ^ a b Taniguchi, Yoshi (23 June 2008). "Star Forming Galaxies at z > 5". Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. 3 (S250): 429–436. arXiv:0804.0644. Bibcode:2008IAUS..250..429T. doi:10.1017/S1743921308020796. S2CID 198472.
- ^ a b Taniguchi, Yoshiaki; Ajiki, Masaru; Nagao, Tohru; Shioya, Yasuhiro; Murayama, Takashi; Kashikawa, Nobunari; et al. (2005). "The SUBARU Deep Field Project: Lymanα Emitters at a Redshift of 6.6" (PDF). Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 57: 165–182. arXiv:astro-ph/0407542. Bibcode:2005PASJ...57..165T. doi:10.1093/pasj/57.1.165.
- ^ a b "Most distant galaxy detected". BBC News. 25 March 2003.
- ^ a b "Subaru Telescope Detects the Most Distant Galaxy Yet and Expects Many More". SpaceRef. March 24, 2003. Archived from the original on 2012-12-09.
- ^ Kodaira, K.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kashikawa, N.; Kaifu, N.; Ando, H.; Karoji, H.; et al. (2003). "The Discovery of Two Lyman$α$ Emitters Beyond Redshift 6 in the Subaru Deep Field". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 55 (2): L17. arXiv:astro-ph/0301096. Bibcode:2003PASJ...55L..17K. doi:10.1093/pasj/55.2.L17.
- ^ "New record for Universe's most distant object". New Scientist. 14 March 2002.
- ^ "Far away stars light early cosmos". BBC News. 14 March 2002.
- ^ Hu, E. M. (2002). "A Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy behind the Cluster Abell 370". The Astrophysical Journal. 568 (2): L75 – L79. arXiv:astro-ph/0203091. Bibcode:2002ApJ...568L..75H. doi:10.1086/340424.
- ^ "K2.1 HCM 6A — Discovery of a redshift z = 6.56 galaxy lying behind the cluster Abell 370". Hera.ph1.uni-koeln.de. 2008-04-14. Archived from the original on 2011-05-18. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ^ Pentericci, L.; Fan, X.; Rix, H. W.; Strauss, M. A.; Narayanan, V. K.; Richards, G T.; Schneider, D. P.; Krolik, J.; Heckman, T.; Brinkmann, J.; Lamb, D. Q.; Szokoly, G. P. (2002). "VLT observations of the z = 6.28 quasar SDSS 1030+0524". The Astronomical Journal. 123 (5): 2151. arXiv:astro-ph/0112075. Bibcode:2002AJ....123.2151P. doi:10.1086/340077. S2CID 119041760.
- ^ Haiman, Zoltan; Cen, Renyue (20 October 2002). "A Constraint on the Gravitational Lensing Magnification and Age of the Redshift z = 6.28 Quasar SDSS 1030+0524 doi=10.1086/342610". The Astrophysical Journal. 578 (2): 702–707. doi:10.1086/342610.
{{cite journal}}: Missing pipe in:|title=(help) - ^ White, Richard L.; Becker, Robert H.; Fan, Xiaohui; Strauss, Michael A. (2003). "Probing the Ionization State of the Universe atz>6". The Astronomical Journal. 126 (1): 1–14. arXiv:astro-ph/0303476. Bibcode:2003AJ....126....1W. doi:10.1086/375547. S2CID 51505828.
- ^ Farrah, D.; Priddey, R.; Wilman, R.; Haehnelt, M.; McMahon, R. (2004). "The X-Ray Spectrum of the z = 6.30 QSO SDSS J1030+0524". The Astrophysical Journal. 611 (1): L13 – L16. arXiv:astro-ph/0406561. Bibcode:2004ApJ...611L..13F. doi:10.1086/423669. S2CID 14854831.
- ^ a b "Discovery Announced of Two Most Distant Objects". Eberly College of Science, Penn State University. 5 June 2001. Archived from the original on 2007-11-21.
- ^ a b "Early results from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey: From under our nose to the edge of the universe". Space News (Press release). SDSS. 5 June 2001.
- ^ a b c d "International Team of Astronomers Finds Most Distant Object". Science Journal. 17 (1). Eberly College of Science, Penn State University. Summer 2000. Archived from the original on 2009-09-12.
- ^ a b Hu, Esther M.; McMahon, Richard G.; Cowie, Lennox L. (1999-09-01). "An Extremely Luminous Galaxy at z = 5.74". The Astrophysical Journal. 522 (1): L9 – L12. arXiv:astro-ph/9907079. Bibcode:1999ApJ...522L...9H. doi:10.1086/312205.
- ^ "X-rays from the Most Distant Quasar Captured with the XMM-Newton Satellite". Eberly College of Science, Penn State University. 1 December 2000. Archived from the original on 2007-11-21.
- ^ "Confirmed High Redshift (z > 5.5) Galaxies". University of Wisconsin-Madison. 10 February 2005. Archived from the original on 2007-06-18.
- ^ Lloyd, Robin (1 December 2000). "Most Distant Object in Universe Comes Closer". Space.com. Archived from the original on 2009-12-09.
- ^ a b c d e f Stern, Daniel; Spinrad, Hyron (December 1999). "Search Techniques for Distant Galaxies". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 111 (766): 1475–1502. arXiv:astro-ph/9912082. Bibcode:1999PASP..111.1475S. doi:10.1086/316471.
- ^ Wilford, John Noble (October 20, 1998). "Peering Back in Time, Astronomers Glimpse Galaxies Aborning". The New York Times.
- ^ a b "A Baby Galaxy". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA. March 24, 1998.
- ^ a b Dey, Arjun; Spinrad, Hyron; Stern, Daniel; Graham, James R.; Chaffee, Frederic H. (1998). "A Galaxy at z = 5.34". The Astrophysical Journal. 498 (2): L93. arXiv:astro-ph/9803137. Bibcode:1998ApJ...498L..93D. doi:10.1086/311331.
- ^ "A New Most Distant Object: z = 5.34". Astro.ucla.edu. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ^ "Behind CL1358+62: A New Farthest Object". Astronomy Picture of the Day. NASA. July 31, 1997.
- ^ Franx, Marijn; Illingworth, Garth D.; Kelson, Daniel D.; Van Dokkum, Pieter G.; Tran, Kim-Vy (1997). "A Pair of Lensed Galaxies at z = 4.92 in the Field of CL 1358+62". The Astrophysical Journal. 486 (2): L75. arXiv:astro-ph/9704090. Bibcode:1997ApJ...486L..75F. doi:10.1086/310844. S2CID 14502310.
- ^ a b c d e f Illingworth, Garth (1999). "Galaxies at High Redshift". Astrophysics and Space Science. 269/270: 165–181. arXiv:astro-ph/0009187. Bibcode:1999Ap&SS.269..165I. doi:10.1023/a:1017052809781. S2CID 119363931.
- ^ Schneider, Donald P.; Schmidt, Maarten; Gunn, James E. (September 1991). "PC 1247 + 3406 - an optically selected quasar with a redshift of 4.897". The Astronomical Journal. 102: 837. Bibcode:1991AJ....102..837S. doi:10.1086/115914.
- ^ Smith, J. D.; Djorgovski, S.; Thompson, D.; Brisken, W. F.; Neugebauer, G.; Matthews, K.; Meylan, G.; Piotto, G.; Suntzeff, N. B. (1994). "Multicolor detection of high-redshift quasars, 2: Five objects with Z greater than or approximately equal to 4" (PDF). The Astronomical Journal. 108: 1147. Bibcode:1994AJ....108.1147S. doi:10.1086/117143.
- ^ Croswell, Ken (10 October 1992). "Science: Infant galaxy's light show". New Scientist. No. 1842. p. 17.
- ^ "Scientists of Sloan Digital Sky Survey Discover Most Distant Quasar" (Press release). FermiLab. December 8, 1998. Archived from the original on 2009-09-12.
- ^ a b Hook, Isobel M.; McMahon, Richard G. (1998). "Discovery of radio-loud quasars with z = 4.72 and z = 4.01". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 294 (1): L7 – L12. arXiv:astro-ph/9801026. Bibcode:1998MNRAS.294L...7H. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1998.01368.x.
- ^ a b c d e Turner, Edwin L. (1991). "Quasars and galaxy formation. I – the Z greater than 4 objects". Astronomical Journal. 101: 5. Bibcode:1991AJ....101....5T. doi:10.1086/115663.
- ^ SIMBAD, Object query : PC 1158+4635, QSO B1158+4635 – Quasar
- ^ Cowie, Lennox L. (1991). "Young Galaxies". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 647 (1 Texas/ESO–Cer): 31–41. Bibcode:1991NYASA.647...31C. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb32157.x. S2CID 222074763.
- ^ a b New York Times, Peering to Edge of Time, Scientists Are Astonished, November 20, 1989
- ^ a b c Warren, S. J.; Hewett, P. C.; Osmer, P. S.; Irwin, M. J. (1987). "Quasars of redshift z = 4.43 and z = 4.07 in the South Galactic Pole field". Nature. 330 (6147): 453. Bibcode:1987Natur.330..453W. doi:10.1038/330453a0. S2CID 4352819.
- ^ Levshakov, S. A. (1989). "Absorption spectra of quasars". Astrophysics. 29 (2): 657–671. Bibcode:1988Ap.....29..657L. doi:10.1007/BF01005972. S2CID 122978350.
- ^ Wilford, John Noble (January 14, 1988). "Objects Detected in Universe May Be the Most Distant Ever Sighted". The New York Times.
- ^ Wilford, John Noble (May 10, 1988). "Astronomers Peer Deeper Into Cosmos". The New York Times.
- ^ "Object query : Q0000-26". SIMBAD.
- ^ a b c d Schmidt, Maarten; Schneider, Donald P.; Gunn, James E. (1987). "PC 0910 + 5625 – an optically selected quasar with a redshift of 4.04". Astrophysical Journal. 321: L7. Bibcode:1987ApJ...321L...7S. doi:10.1086/184996.
- ^ "Object query : PC 0910+5625". SIMBAD.
- ^ Warren, S. J.; Hewett, P. C.; Irwin, M. J.; McMahon, R. G.; Bridgeland, M. T.; Bunclark, P. S.; Kibblewhite, E. J. (1987). "First observation of a quasar with a redshift of 4". Nature. 325 (6100): 131. Bibcode:1987Natur.325..131W. doi:10.1038/325131a0. S2CID 4335291.
- ^ "Object query : Q0046-293". SIMBAD.
- ^ "Object query : Q1208+1011". SIMBAD.
- ^ Henbest, Nigel (16 November 1991). "Quasar doubles help to fix the Hubble constant". New Scientist.
- ^ "Archived Astronomy News Items, 1972–1997". Ipswich: Orwell Astronomical Society. Archived from the original on 2009-09-12.
- ^ "Object query : PKS 2000-330". SIMBAD.
- ^ a b "History of the OSU Radio Observatory". OSU Big Ear.
- ^ "Object query : OQ172". SIMBAD.
- ^ a b c "Quasars – Three Years Later". Archived from the original on 2017-01-18. Retrieved 2010-02-17.
- ^ "The Edge of Night". Time. April 23, 1973. Archived from the original on 2008-12-14.
- ^ "QSO B0642+449 – Quasar". SIMBAD.
- ^ Warren, S. J.; Hewett, P. C. (1990). "The detection of high-redshift quasars". Reports on Progress in Physics. 53 (8): 1095. Bibcode:1990RPPh...53.1095W. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/53/8/003. S2CID 250880776.
- ^ a b Larson, Dewey Bernard (1984). "Chapter 23 – Quasar Redshifts". The Structure of the Physical Universe. Vol. III: The Universe of Motion. North Pacific Publishers. ISBN 0-913138-11-8. Archived from the original on 2008-06-19.
- ^ Bahcall, John N.; Oke, J. B. (1971). "Some Inferences from Spectrophotometry of Quasi-Stellar Sources". Astrophysical Journal. 163: 235. Bibcode:1971ApJ...163..235B. doi:10.1086/150762.
- ^ a b c Lynds, R.; Wills, D. (1970). "The Unusually Large Redshift of 4C 05.34". Nature. 226 (5245): 532. Bibcode:1970Natur.226..532L. doi:10.1038/226532a0. PMID 16057373. S2CID 28297458.
- ^ "7C 105517.75+495540.95 – Quasar". SIMBAD.
- ^ a b Burbidge, Geoffrey (1968). "The Distribution of Redshifts in Quasi-Stellar Objects, N-Systems and Some Radio and Compact Galaxies". Astrophysical Journal. 154: L41. Bibcode:1968ApJ...154L..41B. doi:10.1086/180265.
- ^ "A Farther-Out Quasar". Time. April 7, 1967. Archived from the original on 2008-12-15.
- ^ "Object query : QSO B0237-2321". SIMBAD.
- ^ a b c d Burbidge, Geoffrey (1967). "On the Wavelengths of the Absorption Lines in Quasi-Stellar Objects". Astrophysical Journal. 147: 851. Bibcode:1967ApJ...147..851B. doi:10.1086/149072.
- ^ a b Time Magazine, The Man on the Mountain, Friday, Mar. 11, 1966
- ^ SIMBAD, Object query : Q1116+12, 4C 12.39 – Quasar
- ^ SIMBAD, Object query : Q0106+01, 4C 01.02 – Quasar
- ^ Time Magazine, Toward the Edge of the Universe, Friday, May. 21, 1965
- ^ Time Magazine, The Quasi-Quasars, Friday, Jun. 18, 1965
- ^ The Cosmic Century: A History of Astrophysics and Cosmology p. 379 by Malcolm S. Longair – 2006
- ^ Schmidt, Maarten (1965). "Large Redshifts of Five Quasi-Stellar Sources". Astrophysical Journal. 141: 1295. Bibcode:1965ApJ...141.1295S. doi:10.1086/148217.
- ^ The Discovery of Radio Galaxies and Quasars, 1965
- ^ Schmidt, Maarten; Matthews, Thomas A. (1965). "Redshifts of the Quasi-Stellar Radio Sources 3c 47 and 3c 147". Quasi-Stellar Sources and Gravitational Collapse: 269. Bibcode:1965qssg.conf..269S.
- ^ Schneider, Donald P.; Van Gorkom, J. H.; Schmidt, Maarten; Gunn, James E. (1992). "Radio properties of optically selected high-redshift quasars. I – VLA observations of 22 quasars at 6 CM". Astronomical Journal. 103: 1451. Bibcode:1992AJ....103.1451S. doi:10.1086/116159.
- ^ "Astronomy: Finding the Fastest Galaxy: 76,000 Miles per Second". Time Magazine. Vol. 83, no. 15. April 10, 1964.
- ^ Schmidt, Maarten; Matthews, Thomas A. (1964). "Redshift of the Quasi-Stellar Radio Sources 3c 47 and 3c 147". Astrophysical Journal. 139: 781. Bibcode:1964ApJ...139..781S. doi:10.1086/147815.
- ^ "The Discovery of Radio Galaxies and Quasars". Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ^ McCarthy, Patrick J. (1993). "High Redshift Radio Galaxies". Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics. 31: 639–688. Bibcode:1993ARA&A..31..639M. doi:10.1146/annurev.aa.31.090193.003231.
- ^ a b Sandage, Allan (1961). "The Ability of the 200-INCH Telescope to Discriminate Between Selected World Models". Astrophysical Journal. 133: 355. Bibcode:1961ApJ...133..355S. doi:10.1086/147041.
- ^ Hubble, E. P. (1953). "The law of red shifts (George Darwin Lecture)". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 113 (6): 658–666. Bibcode:1953MNRAS.113..658H. doi:10.1093/mnras/113.6.658.
- ^ Sandage, Allan. "Observational Tests of World Models: 6.1. Local Tests for Linearity of the Redshift-Distance Relation". Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1988 (26): 561–630.
- ^ Humason, M. L.; Mayall, N. U.; Sandage, A. R. (1956). "Redshifts and magnitudes of extragalactic nebulae". Astronomical Journal. 61: 97. Bibcode:1956AJ.....61...97H. doi:10.1086/107297.
- ^ a b c "1053 May 8 meeting of the Royal Astronomical Society". The Observatory. 73: 97. 1953. Bibcode:1953Obs....73...97.
- ^ Merrill, Paul W. (1958). "From Atoms to Galaxies". Astronomical Society of the Pacific Leaflets. 7 (349): 393. Bibcode:1958ASPL....7..393M.
- ^ a b Humason, M. L. (January 1936). "The Apparent Radial Velocities of 100 Extra-Galactic Nebulae". The Astrophysical Journal. 83: 10. Bibcode:1936ApJ....83...10H. doi:10.1086/143696.
- ^ "The First 50 Years At Palomar: 1949–1999; The Early Years of Stellar Evolution, Cosmology, and High-Energy Astrophysics'; 5.2.1. The Mount Wilson Years; Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1999. 37: 445–486
- ^ a b Chant, C. A. (1 April 1932). "Notes and Queries (Doings at Mount Wilson-Ritchey's Photographic Telescope-Infra-red Photographic Plates)". Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. 26: 180. Bibcode:1932JRASC..26..180C.
- ^ Humason, Milton L. (July 1931). "Apparent Velocity-Shifts in the Spectra of Faint Nebulae". The Astrophysical Journal. 74: 35. Bibcode:1931ApJ....74...35H. doi:10.1086/143287.
- ^ Hubble, Edwin; Humason, Milton L. (July 1931). "The Velocity-Distance Relation among Extra-Galactic Nebulae". The Astrophysical Journal. 74: 43. Bibcode:1931ApJ....74...43H. doi:10.1086/143323.
- ^ a b Humason, M. L. (1 January 1931). "The Large Apparent Velocities of Extra-Galactic Nebulae". Leaflet of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 1 (37): 149. Bibcode:1931ASPL....1..149H.
- ^ a b Humason, M. L. (1930). "The Rayton short-focus spectrographic objective". Astrophysical Journal. 71: 351. Bibcode:1930ApJ....71..351H. doi:10.1086/143255.
- ^ a b c d Trimble, Virginia (1996). "H_0: The Incredible Shrinking Constant, 1925–1975" (PDF). Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 108: 1073. Bibcode:1996PASP..108.1073T. doi:10.1086/133837. S2CID 122165424.
- ^ "The Berkeley Meeting of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, June 20–21, 1929". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 41 (242): 244. 1929. Bibcode:1929PASP...41..244.. doi:10.1086/123945.
- ^ a b From the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences; Volume 15 : March 15, 1929 : Number 3; The Large Radial Velocity of N. G. C. 7619; January 17, 1929
- ^ The Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada / Journal de la Société Royale D'astronomie du Canada; Vol. 83, No. 6 December 1989 Whole No. 621; EDWIN HUBBLE 1889–1953
- ^ a b National Academy of Sciences; Biographical Memoirs: V. 52 – Vesto Melvin Slipher; ISBN 0-309-03099-4
- ^ Bailey, S. I. (1920). "Comet Skjellerup". Harvard College Observatory Bulletin. 739: 1. Bibcode:1920BHarO.739....1B.
- ^ New York Times, DREYER NEBULA NO. 584 Inconceivably Distant; Dr. Slipher Says the Celestial Speed Champion Is 'Many Millions of Light Years' Away.; January 19, 1921, Wednesday
- ^ a b New York Times, Nebula Dreyer Breaks All Sky Speed Records; Portion of the Constellation of Cetus Is Rushing Along at Rate of 1,240 Miles a Second.; January 18, 1921, Tuesday
- ^ Hawera & Normanby Star, "Items of Interest", 29 December 1910, Volume LX, page 3 . Retrieved 25 March 2010.
- ^ Evening Star (San Jose), "Colossal Arcturus", Pittsburgh Dispatch, 10 June 1910 . Retrieved 25 March 2010.
- ^ Nelson Evening Mail, "British Bloodthirstiness", 2 November 1891, Volume XXV, Issue 230, Page 3 . Retrieved 25 March 2010.
- ^ "Handbook of astronomy", Dionysius Lardner & Edwin Dunkin, Lockwood & Co. (1875), p.121
- ^ "The Three Heavens", Josiah Crampton, William Hunt and Company (1876), p.164
- ^ (in German) Kosmos: Entwurf einer physischen Weltbeschreibung, Volume 4, Alexander von Humboldt, J. G. Cotta (1858), p.195
- ^ "Outlines of Astronomy", John F. W. Herschel, Longman & Brown (1849), ch. 'Parallax of Stars', p.551 (section 851)
- ^ a b c The North American Review, "The Observatory at Pulkowa", FGW Struve, Volume 69 Issue 144 (July 1849)
- ^ The Sidereal Messenger, "Of the Precession of the Equinoxes, Nutation of the Earth's Axis, And Aberration of Light", Vol.1, No. 12, April 1847: 'Derby, Bradley, & Co.' Cincinnati
- ^ SEDS, "Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (July 22, 1784 – March 17, 1846)" Archived February 4, 2012, at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ^ Harper's New Monthly Magazine, "Some Talks of an Astronomer", Simon Newcomb, Volume 0049 Issue 294 (November 1874), pp.827 (accessed 2009-Nov-11)
- ^ Jensen, Joseph B.; Tonry, John L.; Barris, Brian J.; Thompson, Rodger I.; Liu, Michael C.; Rieke, Marcia J.; Ajhar, Edward A.; Blakeslee, John P. (February 2003). "Measuring Distances and Probing the Unresolved Stellar Populations of Galaxies Using Infrared Surface Brightness Fluctuations". Astrophysical Journal. 583 (2): 712–726. arXiv:astro-ph/0210129. Bibcode:2003ApJ...583..712J. doi:10.1086/345430. S2CID 551714.
- ^ Kepple, George Robert; Sanner, Glen W. (1998). The Night Sky Observer's Guide. Vol. 1. Willmann-Bell. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-943396-58-3.
- ^ Fodera-Serio, G.; Indorato, L.; Nastasi, P. (February 1985). "Hodierna's Observations of Nebulae and his Cosmology". Journal for the History of Astronomy. 16 (1): 1–36. Bibcode:1985JHA....16....1F. doi:10.1177/002182868501600101.
- ^ Gavazzi, G.; Boselli, A.; Scodeggio, M.; Pierini, D. & Belsole, E. (1999). "The 3D structure of the Virgo cluster from H-band Fundamental Plane and Tully-Fisher distance determinations". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 304 (3): 595–610. arXiv:astro-ph/9812275. Bibcode:1999MNRAS.304..595G. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02350.x. S2CID 41700753.
- ^ Burnham, Robert Jr (1978). Burnham's Celestial Handbook. Vol. 3: Pavo Through Vulpecula. Dover. pp. 2086–2088. ISBN 978-0-486-23673-5.
- ^ "The OBEY Survey – NGC 584".
- ^ "Distance Results for NGC 0001". NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. Retrieved 2010-05-03.
- ^ Falla, D. F.; Evans, A. (1972). "On the Mass and Distance of the Quasi-Stellar Object 3C 273". Astrophysics and Space Science. 15 (3): 395. Bibcode:1972Ap&SS..15..395F. doi:10.1007/BF00649767. S2CID 124870214.
- ^ Variable Star Of The Season Archived January 23, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Minkowski, R. (1960). "A New Distant Cluster of Galaxies". Astrophysical Journal. 132: 908. Bibcode:1960ApJ...132..908M. doi:10.1086/146994.
- ^ "Exploding star is oldest object seen in universe". CNN. 2009-04-29. Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ^ Krimm, H.; et al. (2009). "GRB 090423: Swift detection of a burst". GCN Circulars. 9198: 1. Bibcode:2009GCN..9198....1K.






